📚 Publications
My full list of publications is available on Google Scholar:
Journal Articles
2025
- A. Moghassemi, L. Timilsina, I. Rahman, A. Arsalan, G. Muriithi, G. Ozkan, B. Papari, C. Edrington, Z. Zhang, “Real-Time Electro-Thermal Management and Data-Driven Degradation Forecasting of Power Electronics Building Blocks in All-Electric Ships,” IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2025.
Abstract
Will be shared once published.
- A. Moghassemi, L. Timilsina, I. Rahman, G. Ozkan, C. Edrington, Z. Zhang, “Finite Control Set Model Predictive Control for Electro-Thermal Management of Power Electronics Building Blocks in All-Electric Ships,” Naval Engineers Journal, 2025.
Abstract
Will be shared once published.
- A. Arsalan, B. Papari, G. Muriithi, L. Timilsina, E. Buraimoh, A. Moghassemi, I. Rahman, A. A. Khan, G. Ozkan, C. Edrington, “Real-Time Deep Learning Based Cyberattack Mitigation in Electric Drive Systems,” IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2025.
Abstract
Will be shared once published.
- I. Rahman, M. Ozden, A. Moghassemi, L. Timilsina, A. Arsalan, E. Buraimoh, G. Ozkan, B. Papari, C. Edrington, “Real-Time Thermal Management Framework for Neutral-Point Clamped Converters in Electric Vehicles Employing Active Thermal Control and Active Cooling,” IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2025.
Abstract
Will be shared once published.
- G. Muriithi, A. Arsalan, A. Moghassemi, A.A. Khan, L. Timilsina, E. Buraimoh, B. Papari, G. Ozkan, C. Edrington, “Real-Time Zero Trust Evaluation Framework for Hybrid Electric Vehicles,” IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2025.
Abstract
Will be shared once published.
- L. Timilsina, P.H. Hoang, A. Moghassemi, E. Buraimoh, A. Arsalan, I. Rahman, G. Ozkan, C. Edrington, “Real-Time Degradation Abatement Technique in Hybrid Electric Vehicle Using Data-Driven Methods,” International Transactions on Electrical Energy Systems, 2025.
Abstract
Will be shared once published.
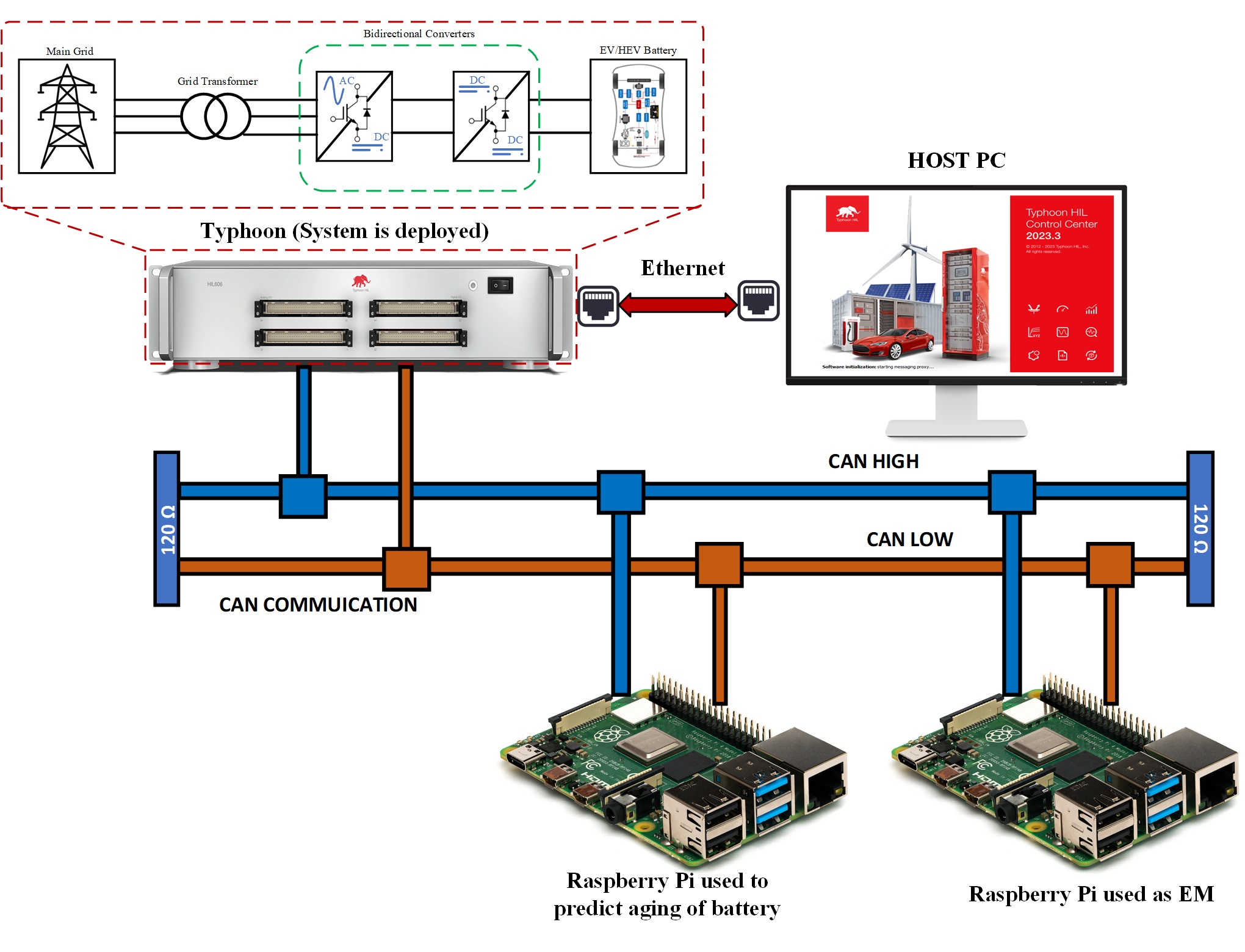
- L. Timilsina, A. Moghassemi, E. Buraimoh, A. Arsalan, I. Rahman, G. Muriithi, G. Ozkan, B. Papari, C. Edrington, “Real-time Analysis of Battery Degradation in a Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles during Vehicle-to-Grid Operation,” SAE Technical Paper, 2025-01-5079, 2025.
doi 🔗Abstract
This paper investigates the impact of Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) integration on battery degradation and the economic viability of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs). V2G technology is gaining traction due to its energy storage capabilities, environmental benefits, and enhancement of grid stability. However, frequent use of the battery in V2G operations can lead to accelerated degradation and increased replacement costs, creating uncertainty for EV owners. This study evaluates battery degradation under two scenarios: driving scenarios using the US06 drive cycle and V2G operation with a 10 kW and 15 kW bidirectional charger. During the V2G operation, the charger discharges the battery by 20 kWh and recharges it back to 90% SoC at a constant 1C rate. Real-time simulations are conducted in order to validate the findings, where a grid, a bidirectional charger, and the vehicle’s battery are all modeled in a real-time simulator. Additionally, a pair of controllers is employed to run the energy management and predict battery aging. An economic analysis assesses the capacity loss from V2G participation and the associated incentives, providing a comprehensive view of the economic feasibility and potential benefits of V2G applications.
Graphical Abstract
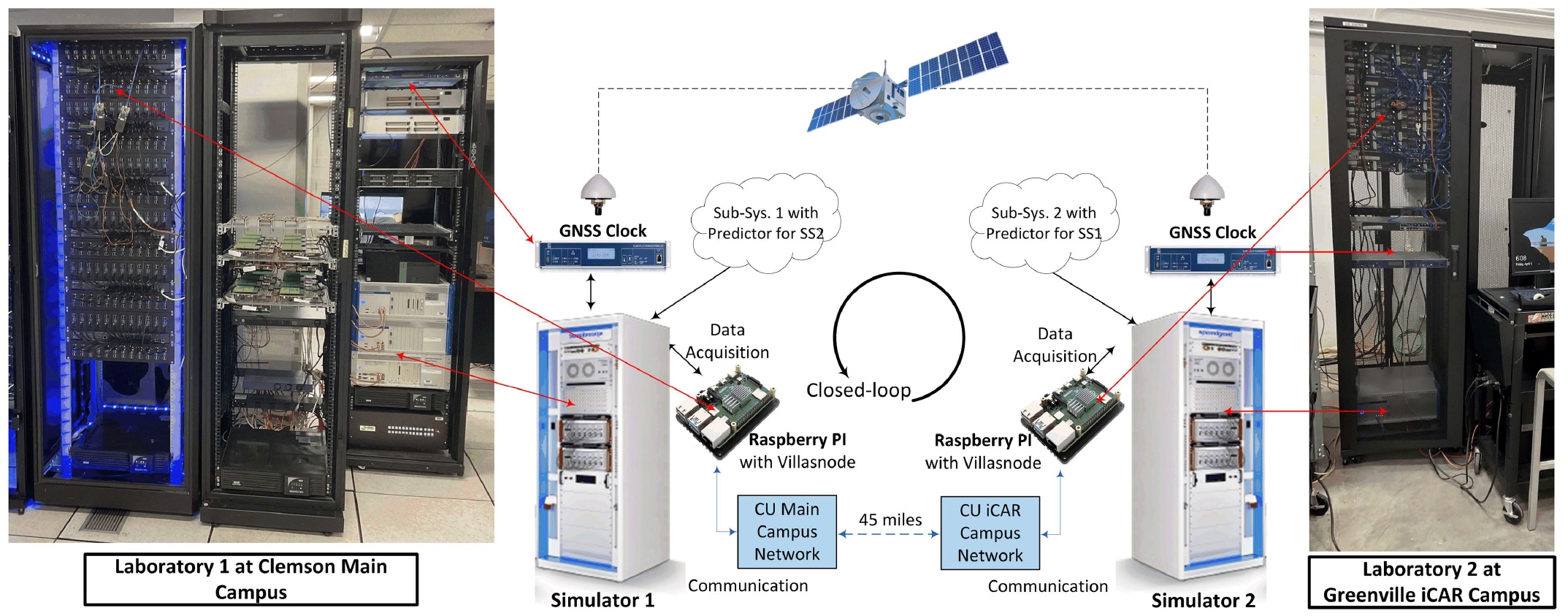
- E. Buraimoh, G. Ozkan, L. Timilsina, I. Rahman, G. Muriithi, A. Moghassemi, A. Arsalan, B. Papari, M. Ozden, C. Edrington, “Adaptive Multi-Parameter Model-Free Delay Compensation for Interface Signals in Distributed Real-Time Co-Simulation of Power Systems,” IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, vol. 40, no. 6, pp. 4932-4944, 2025.
doi 🔗Abstract
Virtual integration of geographically dispersed laboratories through real-time co-simulation presents powerful capabilities for co-simulating massive complex systems but it is hindered by communication delays that compromise accuracy and stability. This challenge is particularly concerning for real-time power system co-simulation, where delays can induce synchronization loss and limit dynamic and transient studies. This study proposes an adaptive, multi-parameter model-free framework for predicting and compensating delays in co-simulated systems, addressing this critical issue. This framework leverages the improved damping impedance method interface algorithm and an adaptive, parameter-tuning predictor system that predicts and compensates for delays without requiring complex interface signal transformation, processing, decomposition, reconstruction, phase estimation, system models, and no human interference. The proposed approach is validated using a joint experiment between two laboratories at Clemson, SC, USA and Greenville, SC, USA, with the Damping Impedance Method as an Interface Algorithm between the two partitioned subsystems. The coupling errors, state tracking errors, and residual complex power are used as evaluation metrics for the proposed delay compensation. This approach enhances co-simulation accuracy and stability, facilitating reliable dynamic and transient analyses.
Graphical Abstract
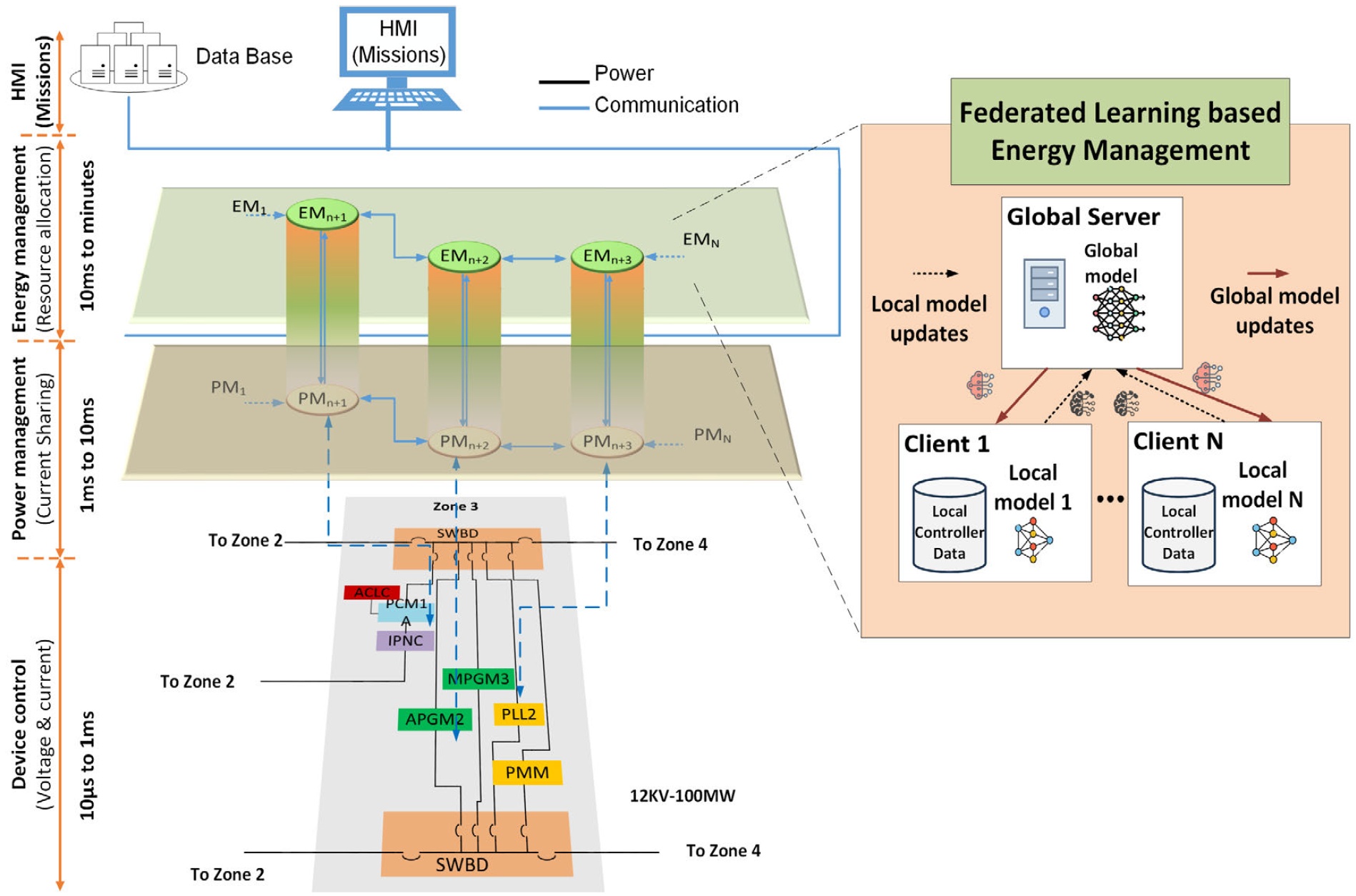
- A. Khan, L. Timilsina, G. Muriithi, A. Arsalan, A. Moghassemi, B. Papari, G. Ozkan, M. Ozden, C. Edrington, N. Boghrabadi, Z. Wang, “Energy Management Systems for Maritime Microgrids: A Comprehensive Review of Intelligent Optimization Strategies,” IEEE Access, vol. 13, pp. 171563-171597, 2025.
doi 🔗Abstract
In modern maritime operations, electric ship power systems (SPSs) play a crucial role as they integrate distributed energy resources to meet stringent environmental targets while ensuring reliability in dynamic and isolated marine environments. Energy management systems (EMS) are critical to optimizing fuel efficiency, reducing emissions, and maintaining power quality under variable load demands and the harsh conditions in which ships operate. This paper presents a comprehensive review of EMS methodologies for SPS, covering traditional methods such as evolutionary algorithms, model predictive control (MPC), fuzzy logic control, and more modern approaches such as machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL). ML and DL for EMS offer predictive and adaptive capabilities for real-time optimization, but face limitations in data security and centralized computational demands. Federated learning (FL), which is a decentralized, privacy-preserving paradigm, is a viable solution to the disadvantages of the conventional centralized form of training in ML. FL enables collaborative model training across distributed systems without raw data sharing, addressing critical concerns in cybersecurity and communication overhead. However, FL does require individual devices or clients to have enough computational power to carry out distributed optimization locally. A detailed overview of FL, including the FL training process, categories, architectures and various applications of FL in ship and energy systems, is presented in this paper. To further establish the usefulness of conducting energy management (EM) in ship systems, the paper presents a case study on a notional four-zone DC SPS in which FL has been utilized to collaboratively train DL models across multiple generators without sharing sensitive local data. The results demonstrate better generator output power prediction and effective load management in comparison to the conventional centralized learning setup, indicating the potential of FL to enhance energy efficiency and reliability in ship systems. Finally, some challenges and possible research gaps in applying FL to ship systems are discussed.
Graphical Abstract
- A. Moghassemi, L. Timilsina, I. Rahman, A. Arsalan, G. Muriithi, E. Buraimoh, G. Ozkan, B. Papari, C. Edrington, Z. Zhang, P.K. Chamarthi, “Real-Time Improved Nearest Level Control for Power Electronics Building Blocks in All-Electric Ship Power Systems,” IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, vol. 61, no. 5, pp. 7656-7670, 2025.
doi 🔗Abstract
Power electronics building block (PEBB) concept involves integrating fundamental components into functional blocks that can be stacked, extending converter power ratings for all-electric ships (AESs). This modular approach reduces costs, size, weight, design complexity, and maintenance. PEBBs can be realized as modular multi-level converters (MMCs), which offer advantages like modularity, low switching losses, minimal voltage/current quantization, high reliability, and efficiency. However, effective switching control methods are crucial to balance capacitor voltages and suppress circulating currents. This paper proposes an improved nearest level control (NLC) method that employs smoothed trapezoidal reference signals instead of sinusoidal references, aiming to enhance capacitor voltage balancing, suppress circulating currents, and improve the output power quality of PEBBs in AESs. The proposed NLC method is analyzed in real-time for an N-level PEBB connected to an induction machine (IM) with variable speed and torque load. The real-time verification is conducted in the Typhoon HIL606 digital real-time simulator (DRTS). The results validate the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed NLC method for a three-phase N-level PEBB concept for AESs.
Graphical Abstract

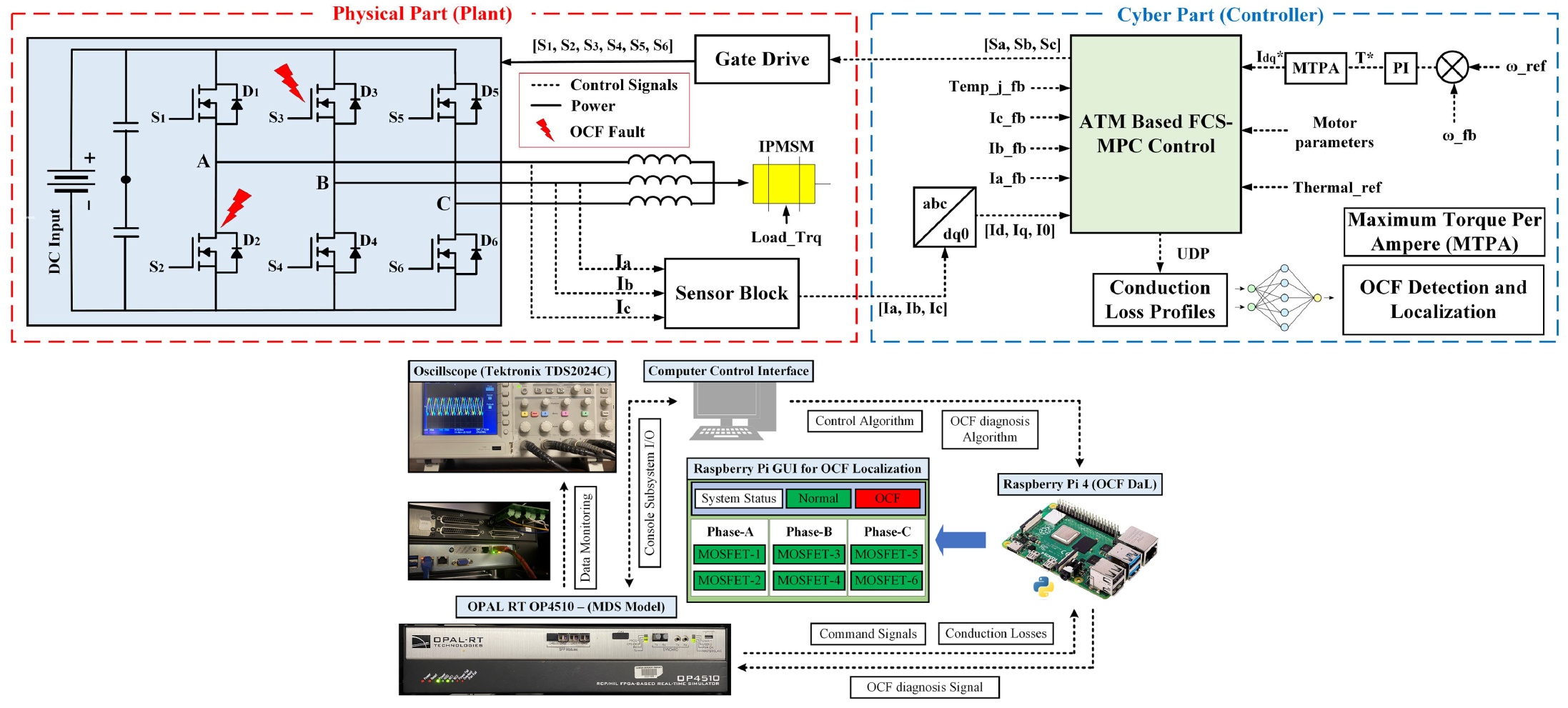
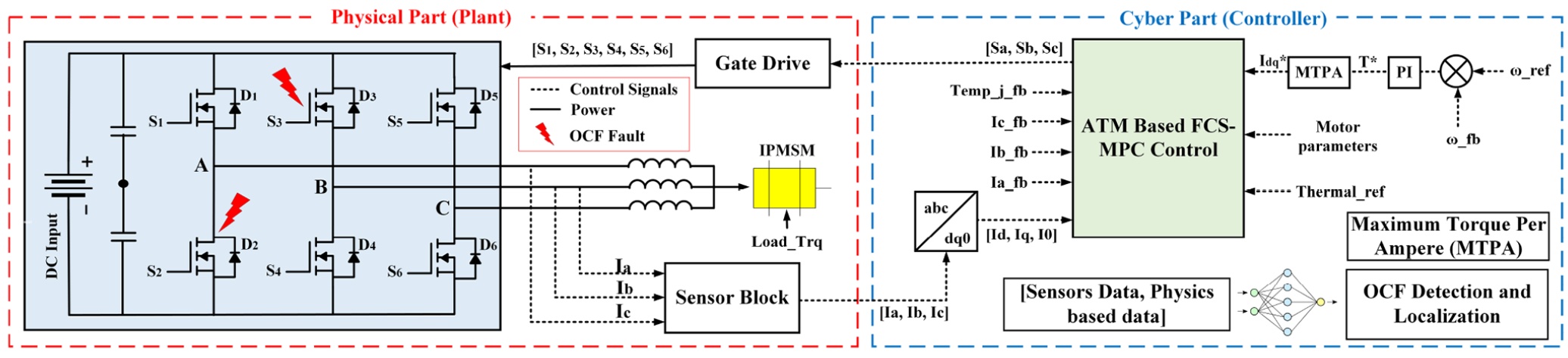
- A. Arsalan, B. Papari, L. Timilsina, G. Muriithi, A. Moghassemi, I. Rahman, E. Buraimoh, G. Ozkan, C. Edrington, “Reliability Score Benchmarking and Resistive Loss Profile-Based Open-Circuit Fault Diagnosis Approach for Motor Drive System,” IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, vol. 40, no. 7, pp. 9824–9839, 2025.
doi 🔗Abstract
In recent years, data-driven methods have shown promise in diagnosing various open circuit fault (OCF) modes in inverter drive applications. However, existing studies primarily evaluate the reliability of these methods based solely on classification accuracy, neglecting critical real-time factors, such as computational delays and data transfer latency associated with the data-driven approach and communication protocols, respectively, which can affect real-time operational reliability. This article addresses these gaps by proposing a universally applicable reliability score criterion that integrates classification accuracy with system timing profiles. In addition, a model predictive control strategy employing active thermal management (ATM) is applied to the drive system, enabling a detailed analysis of the impact of OCF modes on the junction temperature of MOSFETs. Moreover, a novel feature extraction dataset is introduced, leveraging resistive/conduction loss data from the ATM scheme without requiring signal preprocessing. The proposed reliability score quantification and the dataset's diagnostic potential are validated using various data-driven classifiers. The most reliable classifier, achieving a 99.95% diagnosis accuracy, is further tested under diverse operating conditions using a control hardware-in-the-loop setup on an OPAL-RT testbed and Raspberry Pi.
Graphical Abstract
- E. Buraimoh, G. Ozkan, L. Timilsina, G. Muriithi, B. Papari, A. Arsalan, A. Moghassemi, M. Ozden, C. Edrington, “Analysis of Model Free Predictors for Interface Signal Delay Compensation in Real-Time Co-simulation,” IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, vol. 21, no. 4, pp. 3448–3457, 2025.
doi 🔗Abstract
Real-time cosimulation of geographically dispersed laboratories enables extensive system simulations but faces significant challenges from communication delays, impacting accuracy and stability. This issue is crucial in real-time power system cosimulation, where delays can disrupt synchronism and hinder dynamic analyses. This article proposes model-free predictive delay compensation methods as a viable alternative to signal transformation-based methods. This study explores the frequency domain stability of a model-free framework for delay prediction and compensation at power system interfaces using the ideal transformer method as an interface algorithm. Similarly, time-domain implementation reveals signal amplitude magnification, addressed by introducing a delay- and frequency-dependent normalizing factor. This framework adapts interface coupling signals, enabling real-time parameter tuning without complex processing or system models, enhancing co-simulation accuracy and stability for distributed power system analyses.
Graphical Abstract
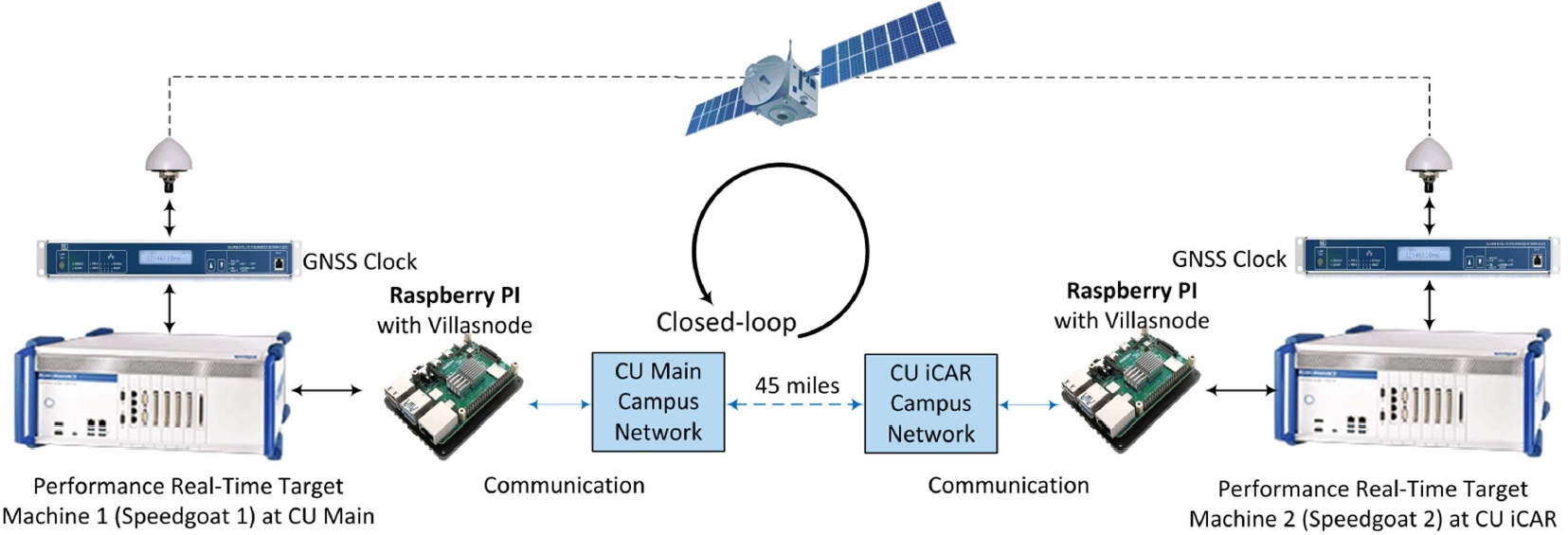
- A. Moghassemi, D.S. Vanaja, J. Olamaei, G. Ozkan, C. Edrington, “A Novel Switching Method in PV Fed Quasi-ZSI-DVR for Voltage Quality Enhancement of Photovoltaic Integrated Networks,” IET Renewable Power Generation, vol. 19, pp. 1–29, 2025.
doi 🔗Abstract
In this work, a novel switching method for the photovoltaic-fed (PV-fed) dynamic voltage restorer (DVR) system based on a quasi-Z-source inverter (quasi-ZSI) is proposed. This proposed switching control strategy is implemented in such a way that a wider voltage boost gain and lower voltage stress across the switches and capacitors are achieved. The major drawback with the traditional switching method is that always three switches will be in conduction. However, in the proposed switching method, only two switches are triggered simultaneously to achieve the required output. It also obviates the need for zero states. The proposed switching method for the PV-fed quasi-ZSI-DVR provides an accurate compensation for various voltage disturbances, such as sags, swells, and interruptions, thereby eliminating the voltage harmonics at the point of common coupling. The integration of PV and battery is suggested for the quasi-ZSI-DVR to tackle the pertinent issue regarding sporadically transferring energy in the PV arrays and also recharging of batteries. Simulation and experimental results validate the suitability of the proposed PV-fed quasi-ZSI-DVR configuration with the proposed switching control method. It is inferred that the proposed system provides the lowest voltage harmonics and additional benefits like smaller capacitors, higher voltage gain, and lower voltage stress rates.
Graphical Abstract
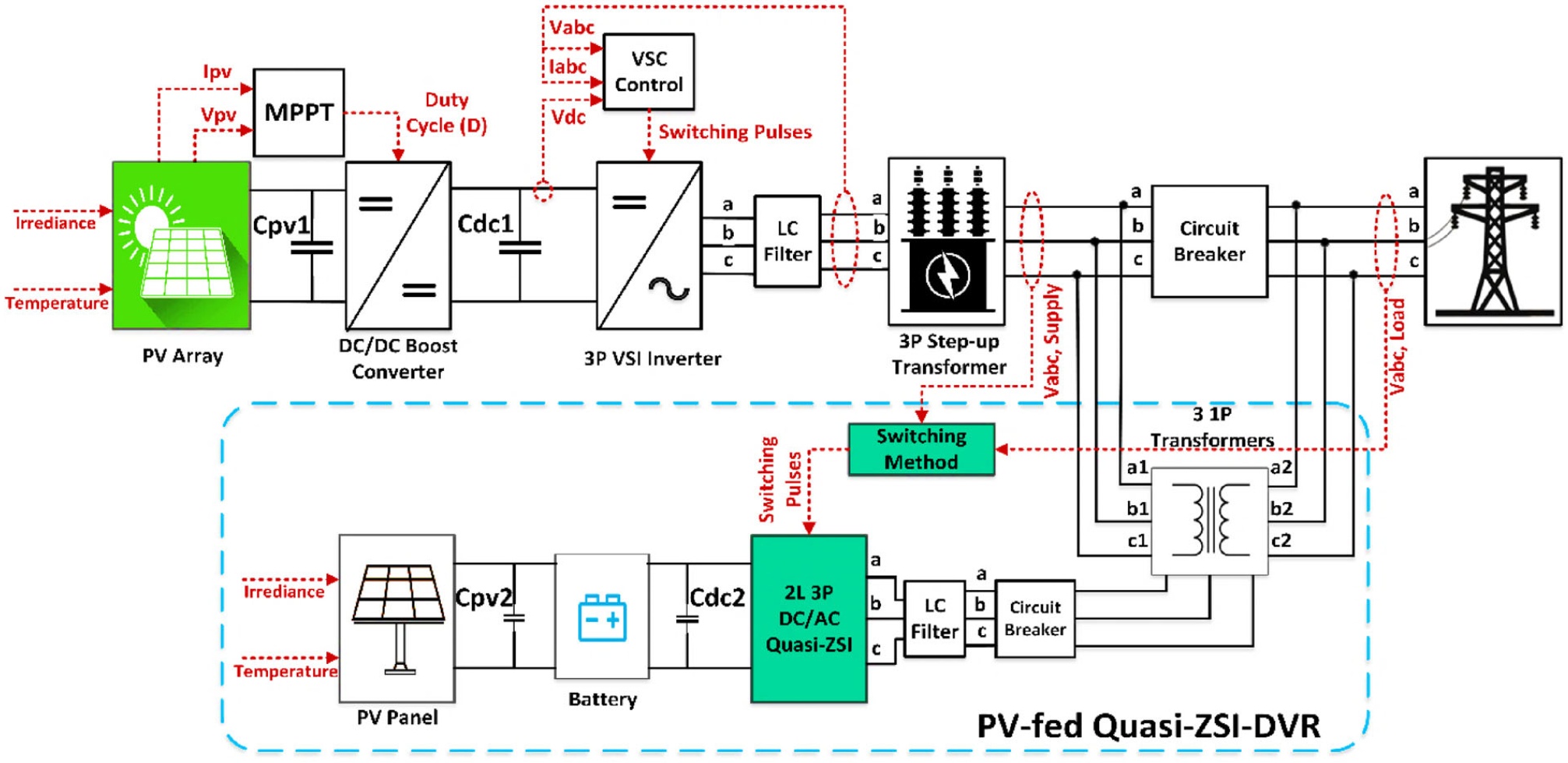
- G. Muriithi, B. Papari, A. Moghassemi, A. Sundar, A. Arsalan, L. Timilsina, G. Ozkan, C. Edrington, “Vulnerability Assessment and Detection of Stealthy Sequential Cyberattacks in Hybrid Tracked Vehicles,” IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 6472–6489, 2025.
doi 🔗Abstract
This article presents an innovative approach to improve hybrid powertrains’ cyber-physical security for high-speed, tracked, off-road vehicles against subtle and sophisticated cyberattacks. While cyber threats against hybrid tracked vehicles (HTVs) have been acknowledged, exploring advanced cyberattacks targeting battery lifetime and energy efficiency within the powertrain remains underexplored. This article proposes a dual-pronged intelligent methodology to construct novel FDIAs targeting vehicle control decisions from the energy management system (EMS). The optimal cyberattack strategy by a minimally informed adversary is formulated as a partial observable Markov decision process (POMDP), employing deep reinforcement learning (DRL) for online learning and attacking. Simultaneously, a comprehensive reward system is devised that incorporates sniffing features to elevate the stealthiness and efficacy of the cyberattacks. This augmentation ensures that the orchestrated attack vectors remain inconspicuous to human drivers. Evaluation metrics are formulated to assess the impact and stealth characteristics of the cyberattack. Furthermore, a sliding window-based controller data monitoring scheme combining iForest and dynamic time warping (DTW) algorithms is proposed to automatically detect the stealthy FDIAs in real-time, ensuring secure control of energy-efficient powertrain systems. Through the proposed metrics and detection module, the article thoroughly examines the impact of cyberattacks on the energy consumption of the HTV. It also provides vital insights for defending vehicles that operate in austere environments against sophisticated controller attacks.
Graphical Abstract
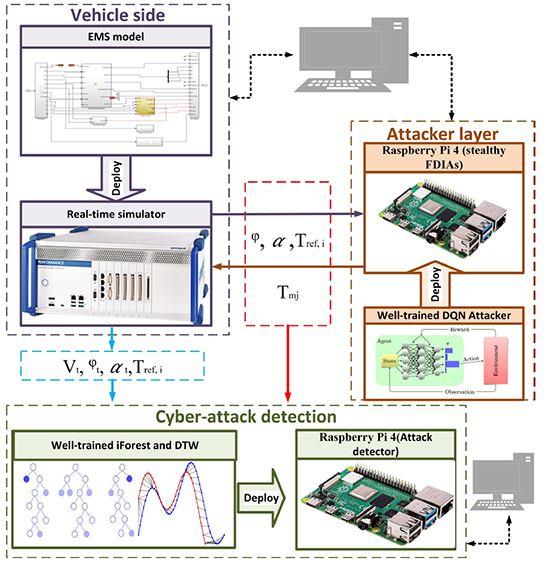
- A. Arsalan, B. Papari, L. Timilsina, G. Muriithi, A. Moghassemi, I. Rahman, E. Buraimoh, G. Ozkan, C. Edrington, “Enhanced Real-Time ATM-Based MPC for Electric Vehicles with Cyber-Physical Security Aspect,” IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 4698–4716, 2025.
doi 🔗Abstract
Inverter-based electric drive systems (EDSs) in electric vehicles (EVs) are susceptible to various common cyber and physical anomalies (CPAs), such as cyberattacks (CAs) and open-circuit faults (OCFs) in power switches. Most existing data-driven diagnostic schemes for motor drives solely rely on residual and three-phase output current signals and are prone to misclassification due to overlapping data features associated with these anomalies. Moreover, these methods concentrate on detecting either CAs or OCFs independently, lacking a unified approach that can be universally applied to both types of anomalies. Therefore, in this work, a physics-informed machine learning (PIML) approach is proposed, which can effectively distinguish between CAs and OCFs in EDS. In this regard, the unique features associated with stator current, resulting from various CPAs, are used to estimate the stator voltage characteristics through a synchronous motor mathematical model. The proposed voltage-based features characterizing better correlation via distinctive EDS transients in response to these anomalies are further used as the system’s prior information by a machine learning (ML) classifier. Moreover, active thermal management (ATM)-based model predictive control (MPC) is utilized in the control layer due to its benefits in device-level thermal cycling and power quality. In addition, various variations in electrical, mechanical, and thermal characteristics due to CPAs in EDS have also been analyzed. The presented approach is evaluated for the US06 standard drive cycle in real time via a controller-hardware-in-the-loop (CHIL) experiment for various case study scenarios, resulting in a classification accuracy of 98.92%.
Graphical Abstract

2024
- B. Papari, L. Timilsina, A. Moghassemi, A.A. Khan, A. Arsalan, G. Ozkan, C. Edrington, “Advanced Meta Metrics-Based Approach to Assess an Appropriate Optimization Method for Wind/PV/Battery Based Hybrid AC-DC Microgrid,” e-Prime - Advances in Electrical Engineering, Electronics and Energy, p. 100640, 2024.
doi 🔗Abstract
This paper discusses the growing influence of renewable energy and distributed generation, emphasizing the need for smart control systems to maximize benefits and optimize network performance. However, the absence of a standardized evaluation framework makes it challenging to compare different control systems effectively, especially in large-scale hybrid networks with both AC and DC components. While hybrid energy systems show promise for greener and more reliable power networks, they introduce complexity to control methods. Researchers are exploring innovative approaches, including linear and nonlinear techniques, to leverage renewable energy sources effectively in hybrid grids. The paper provides an overview of heuristic evolutionary optimization methods for microgrids (AC, DC, and hybrid AC-DC), highlighting promising techniques such as Crow Search Algorithm, Modified Crow Search Algorithm, Particle Swarm Optimization, and Genetic Algorithms. Comparative analysis suggests that the Modified Crow Search Algorithm performs best across various evaluation criteria, indicating its potential for optimizing microgrids effectively.
Graphical Abstract
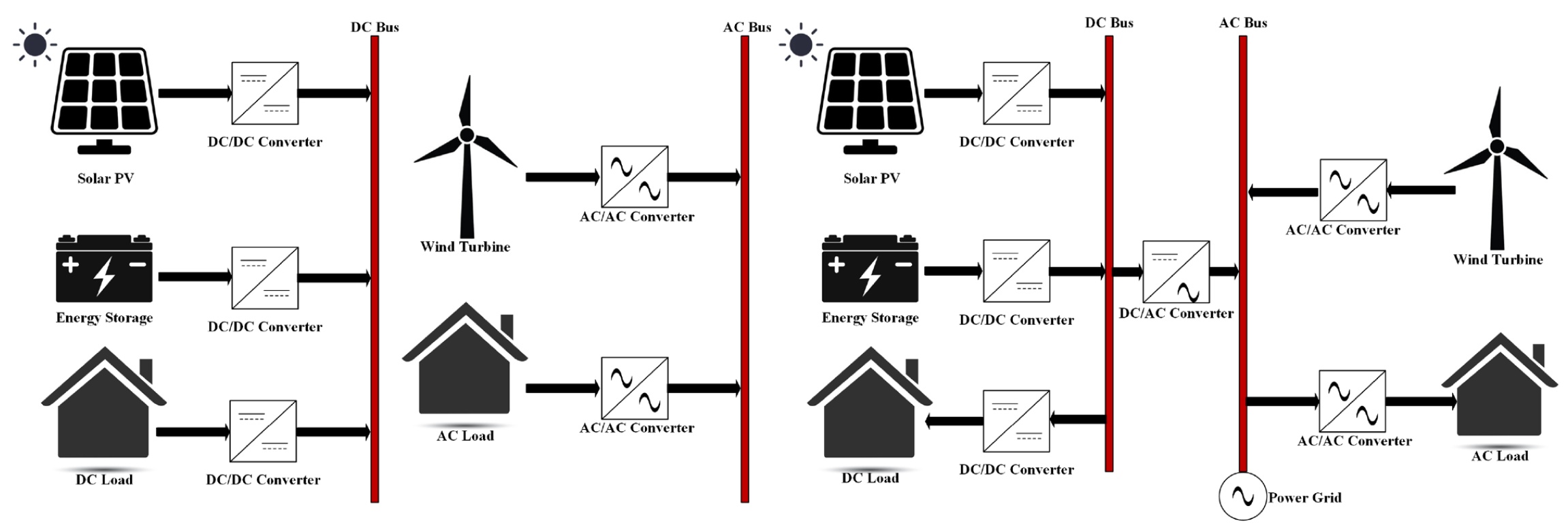
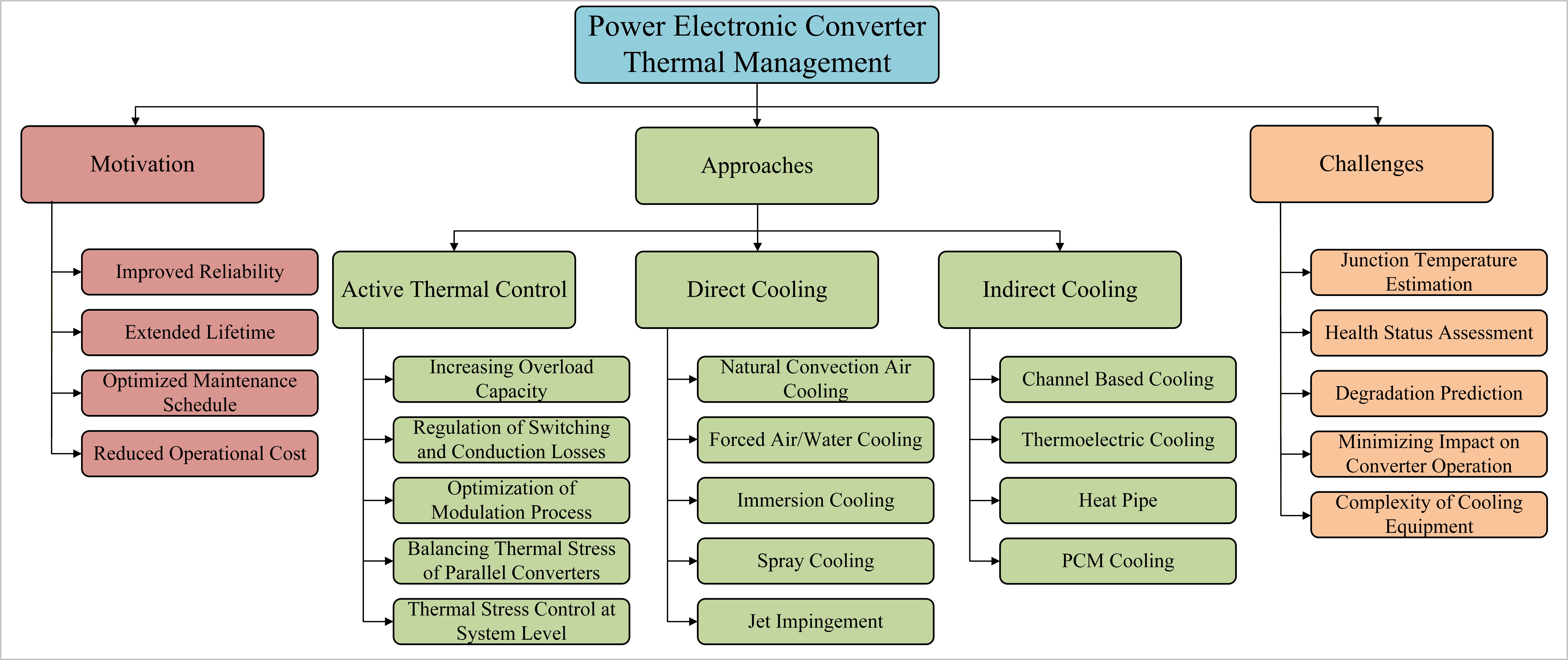
- I. Rahman, A. Moghassemi, P.K. Chamarthi, G. Ozkan, C. Edrington, B. Papari, “Emerging Trends and Challenges in Thermal Management of Power Electronic Converters: A State of The Art Review,” IEEE Access, vol. 12, pp. 50633–50672, 2024.
doi 🔗Abstract
Recently, the thermal management of power electronic converters has gained significant attention due to the continuous trend of developing very compact power electronic converters with high power density. With the evolution of power semiconductor devices, high operating temperatures and large thermal cycles have become possible, necessitating a significant improvement in thermal system designs. Researchers have made significant efforts to develop effective thermal management systems to improve the reliability and lifetime of power electronic converters. This article intends to present a thorough review of thermal management systems employed in power electronics cooling. The applied thermal management techniques have been reviewed from the perspective of electrical parameter regulation and heat dissipation control. Regulation of electrical parameters involves active thermal control, which is a method for controlling junction temperature and thermal cycling of power semiconductor devices. The active thermal control implementation processes reviewed in this article consist of increasing overload capacity, manipulating switching and conduction losses, employing modified modulation processes, balancing thermal stress at the converter level, and controlling thermal stress at the system level. Control of heat dissipation can be achieved through direct and indirect cooling of power electronic converters with air or liquid as the coolant. The effectiveness and implementation methods of these cooling techniques, such as channel cooling, phase change material-based cooling, immersion cooling, jet impingement and spray cooling, are reviewed in this paper. Moreover, performance-enhancing ideas and challenges for these techniques are discussed. The primary objective of this review paper is to bridge the existing gap in the literature by offering a comprehensive comparison of commonly employed thermal management techniques.
Graphical Abstract
2023
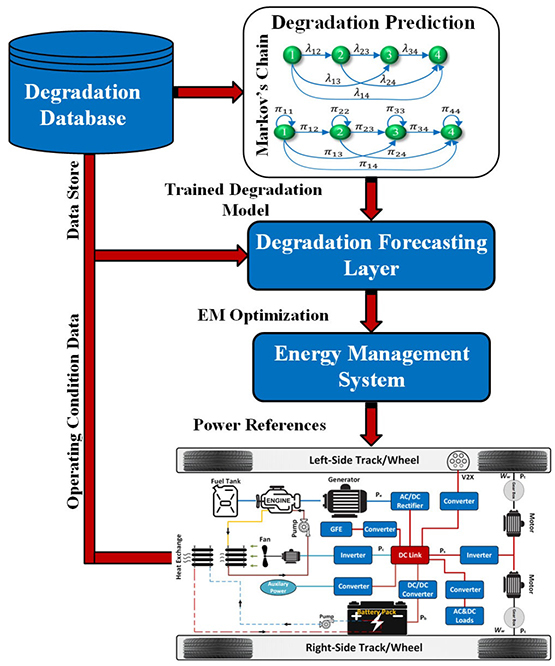
- L. Timilsina, P.H. Hoang, A. Moghassemi, G. Ozkan, B. Papari, C. Edrington, “A Real-Time Prognostic Based Control Framework for Hybrid Electric Vehicles,” IEEE Access, vol. 11, pp. 127589–127607, 2023.
doi 🔗Abstract
The increasing popularity of electric vehicles is driven by their compatibility with sustainable energy goals. However, the decline in the performance of energy storage systems, such as batteries, due to their degradation puts electric vehicles and hybrid electric vehicles at a disadvantage compared to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. This paper presents a prognostic-based control framework for hybrid electric vehicles to reduce the cost of operating hybrid electric vehicles by considering the degradation of energy storage systems. The strategy utilizes a degradation forecasting model of electrical components to predict their degradation pattern and uses the prediction to control hybrid electric vehicles via their energy management systems to reduce the degradation of components. A real-time controller hardware-in-the-loop is set up to run the proposed strategy. A hybrid electric vehicle model is developed on Typhoon (i.e., a real-time simulator), which is connected to two layers: energy management and degradation forecasting layer, deployed in Raspberry Pis, respectively. All these components are communicated through CAN communication, where the actual operating condition of the vehicle is sent from Typhoon to each Raspberry Pis to implement the proposed control strategy. With this approach, the cost of operating hybrid electric vehicles can be reduced, making them more competitive than their combustion engine counterparts shown in both numerical simulations and the CHIL experiment.
Graphical Abstract
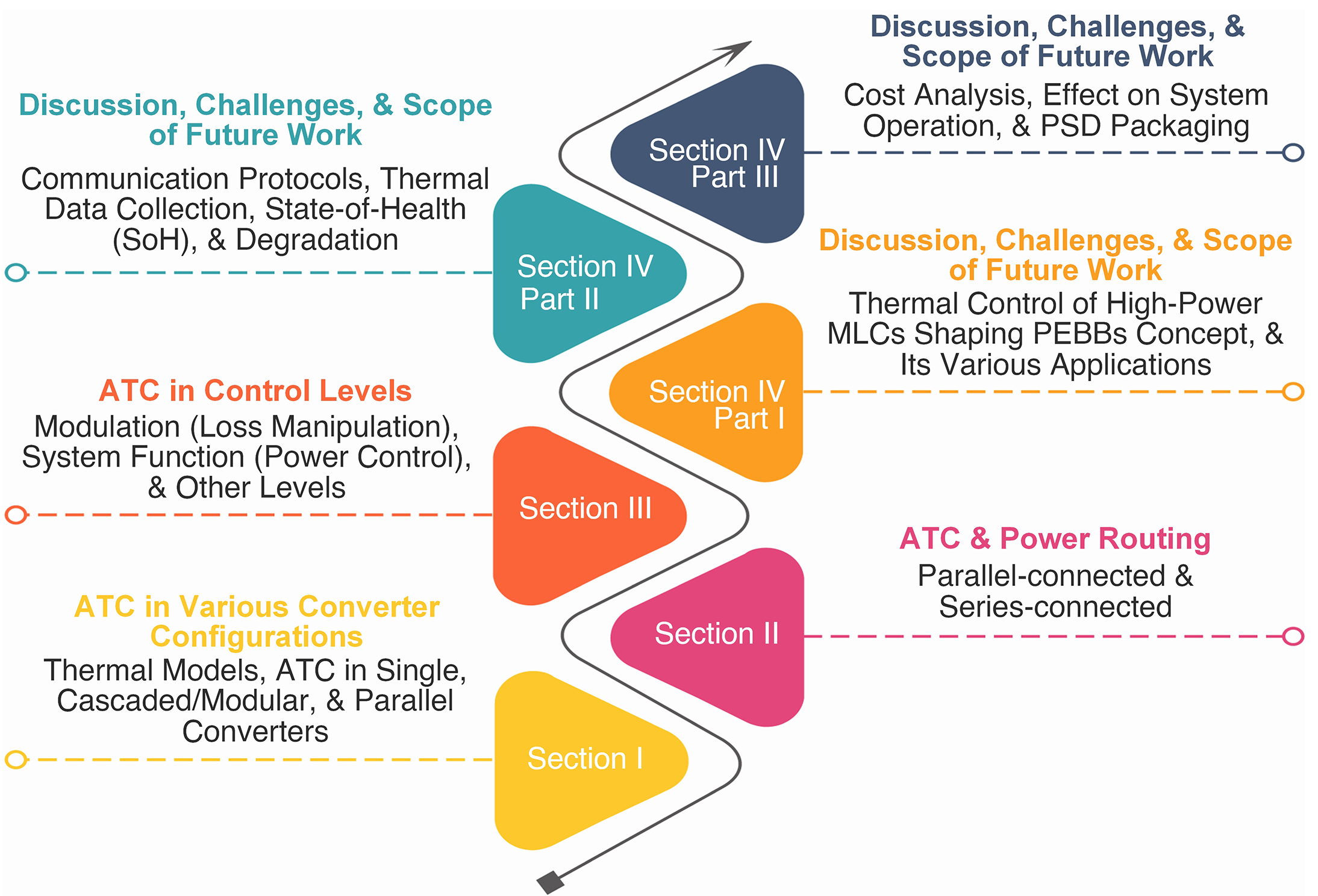
- A. Moghassemi, I. Rahman, G. Ozkan, C. Edrington, Z. Zhang, P.K. Chamarthi, “Power Converters Coolant: Past, Present, Future, And A Path Toward Active Thermal Control in Electrified Ship Power Systems,” IEEE Access, vol. 11, pp. 91620–91659, 2023.
doi 🔗Abstract
Power converters have widespread applications in automotive, renewables, and power systems. The demand for power modules with low power consumption and high efficiency has increased due to advancements in semiconductor devices. So, power converters need to be highly efficient to reduce costs associated with energy dissipation and cooling requirements. This paper discusses various active thermal control methods for high-power power converters. It covers modulation and configuration techniques, ranging from single configurations to cascaded, modular, and multilevel converters. These concepts form the basis of power electronics building blocks, particularly relevant in all-electric ship systems. Power electronics building blocks represent a thriving technology that will advance ship power systems, the thermal design of which plays a crucial role in managing high heat dissipation levels. Hence, thermal management is essential for reliable device performance. The paper thoroughly studies different active thermal control methods and their impact on power semiconductor devices and converters, categorized by configurations, power routing methods, modulation, and control layers. The review then moves to thermal control methods for the PEBBs concept using multilevel converters in all-electric ship systems. The paper eventually outlines future research directions for the thermal aspect of power electronics building blocks.
Graphical Abstract
2022
- A. Moghassemi, S. Ebrahimi, S. Padmanaban, M. Mitolo, J. Holm-Nielsen, “Two Fast Metaheuristic Based MPPT Techniques for Partially Shaded Photovoltaic System,” International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, vol. 137, p. 107567, 2022.
doi 🔗Abstract
The photovoltaic output power varies according to the solar radiation and ambient temperature because the operation of the photovoltaic arrays depends on them. Therefore, achieving the maximum photovoltaic power under different shading patterns is a key factor in the performance improvement of photovoltaic systems. An efficient Maximum Power Point Tracking technique is needed to distinguish the global maximum power point from the local ones, as the traditional techniques are prone to fail. This paper proposes two hybrid meta-heuristic algorithms to improve the maximum power point tracking technique of partially shaded photovoltaic systems. The first proposed maximum power point tracking technique is based on the Whale Optimization Algorithm and Differential Evolution algorithms. The second proposed maximum power point tracking technique is an improved version of the first proposed technique. Both proposed techniques are highly proficient in enhancing the photovoltaic system’s efficiency in shaded and unshaded conditions. The maximum power point tracking technique is studied for evaluating the performance based on two traditional algorithms, Whale Optimization Algorithm and Differential Evolution, and two hybrid proposed algorithms. The simulation results show the second proposed maximum power point tracking technique finds the global power points faster and offers better performance than the first proposed technique, which itself outperforms two traditional maximum power point tracking techniques concerning a faster rate of convergence and higher efficiency.
Graphical Abstract
2021
- D.S. Vanaja, A.A. Stonier, A. Moghassemi, “A Novel Control Topology for Grid-Integration with Modular Multilevel Inverter,” International Transactions on Electrical Energy Systems, vol. 31, no. 12, p. e13135, 2021.
doi 🔗Abstract
This paper presents a novel control topology for a multilevel inverter with a reduced number of power switches for achieving an increased number of levels in the output voltage, along with improved power quality. The diode clamped multilevel inverter configuration is modified, and the gating signals are generated using a selective harmonic optimization technique at fundamental frequency using Satin Bower Bird optimization (SBO). It enhances the quality of the output voltage waveform with the reduction in total harmonic distortion (THD), less switching power losses, and better efficiency. The inverter is investigated for its competent operation capability on grid-tied applications. A detailed simulation is conducted, and results are presented for various load conditions. To validate the inverter operation, an experimental setup of the modified diode clamped modular inverter (MDCMI) interfacing the grid is presented. The loss analysis is carried out at the inverter and converter segments. Based on the analysis, the proposed control topology demonstrates the reliable and efficient operation of the modular inverter. From the results obtained, it is evident that the proposed inverter design suits suitable for the grid applications.
Graphical Abstract
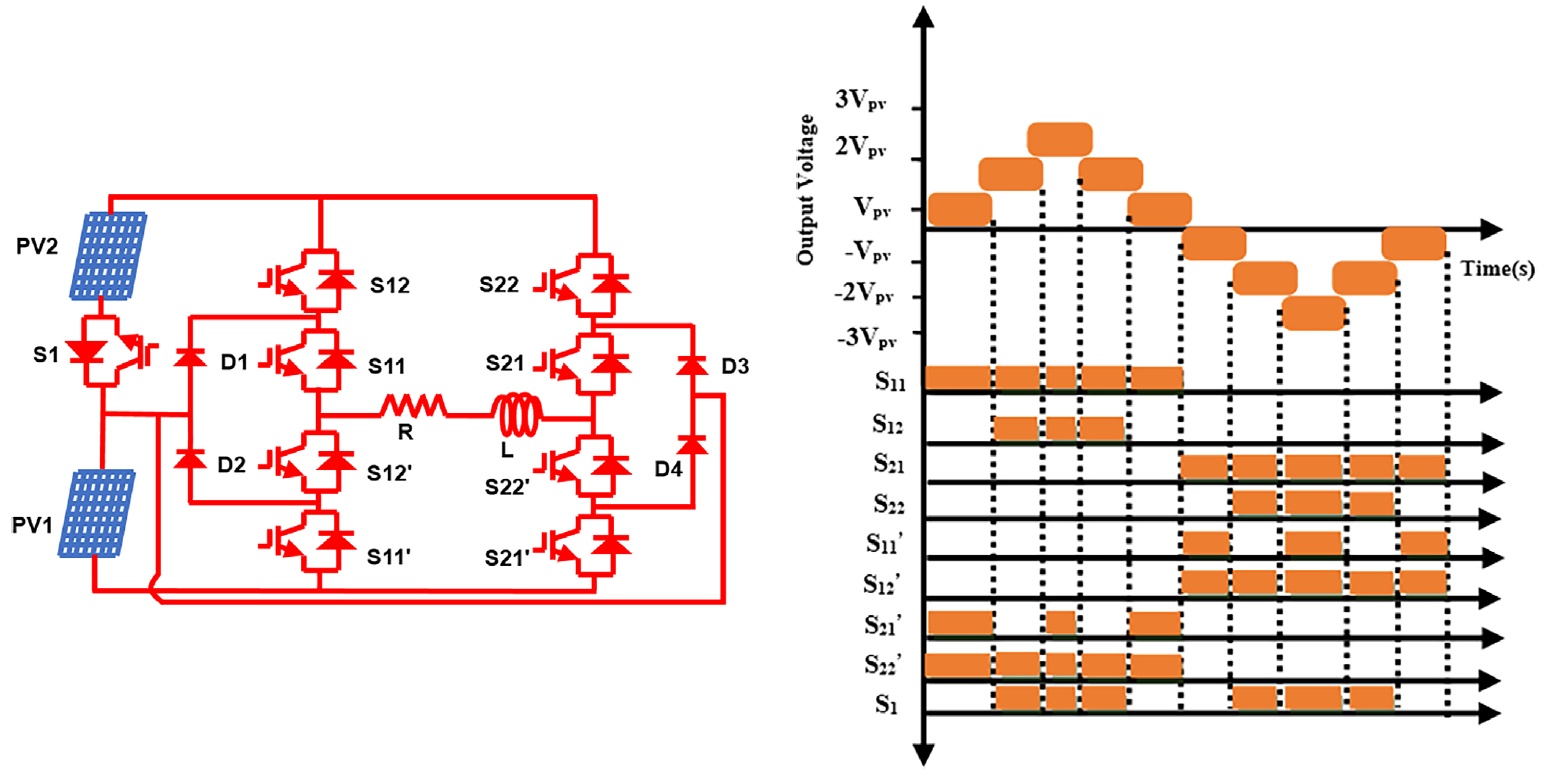
- M. Saadatmand, G. Gharehpetian, A. Moghassemi, J. Guerrero, P. Siano, H. Alhelou, “Damping of Low-Frequency Oscillations in Power Systems by Large-Scale PV Farms: A Comprehensive Review of Control Methods,” IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 72183–72206, 2021.
doi 🔗Abstract
Global warming and the desire to increase the use of clean energy have led to an increase in the installation and operation of renewable energy power plants (REPPs), especially large-scale photovoltaic (PV) farms (LPFs). Given that the LPFs are added to the power system or replace conventional power plants, they must be able to perform the basic tasks of synchronous generators (SGs). One of these tasks is the ability to mitigate the low-frequency oscillation (LFO) risk. Also, one of the LPFs problems is reducing the power system inertia and increasing the risk of LFOs. Therefore, these types of power plants must damp the LFOs through a power oscillation damping controller (PODC), similar to the performance of power system stabilizers (PSSs) in the SGs. This paper represents an overview of the different PODCs and control methods for LFOs damping by LPF. It seems that it can be a driver for future studies. Different studies show that the application of PODCs for LPFs can play an effective role in dampening the LFOs and increasing the power system stability.
Graphical Abstract
2020
- A. Moghassemi, S. Padmanaban, V.K. Ramachandaramurthy, M. Mitolo, M. Benbouzid, “A Novel Solar Photovoltaic Fed TransZSI-DVR for Power Quality Improvement of Grid-Connected PV Systems,” IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 7263–7279, 2020.
doi 🔗Abstract
In this article, a new solar PV-fed Dynamic Voltage Restorer (DVR) based on Trans-Z-source Inverter (TransZSI) is proposed to improve the power quality of on-grid Photovoltaic (PV) systems. DVR is a power electronic compensator used for injecting the desired voltage to the Point of Common Coupling (PCC) as per the voltage disturbance. In the proposed DVR, in place of traditional VSI, TransZSI with outstanding merits of buck/boost, a broader range of voltage boost gain, fewer passive components, and lower voltage stress, is put forth. For efficient detection, accurate voltage disturbances mitigation, and also lessening the injected voltage harmonics, a hybrid Unit Vector Template with Maximum Constant Boost Control (UVT-MCBC) method is proposed for TransZSI-DVR. The performance of the proposed TransZSI-DVR with UVT-MCBC has been analyzed under severe sag, slight sag with harmonics, swell, and interruption. The comparative studies and simulation results have shown the effectiveness of the proposed TransZSI-DVR, as opposed to traditional ZSI-DVR and VSI-DVR. The TransZSI-DVR in the PV system has mitigated voltage sag/swell/interruption. It has also improved the power quality of both the injected voltage to the PCC and the PV system's output voltage.
Graphical Abstract

- A. Moghassemi, S. Padmanaban, “Dynamic Voltage Restorer (DVR): A Comprehensive Review of Topologies, Power Converters, Control Methods, and Modified Configurations,” Energies, vol. 13, no. 16, p. 4152, 2020.
doi 🔗Abstract
Power quality is a pressing concern and of the utmost importance for advanced and high-tech equipment in particular, whose performance relies heavily on the supply’s quality. Power quality issues like voltage sags/swells, harmonics, interruptions, etc., are defined as any deviations in current, voltage, or frequency that result in end-use equipment damage or failure. Sensitive loads like medical equipment in hospitals and health clinics, schools, prisons, etc., malfunction for the outages and interruptions, thereby causing substantial economic losses. For enhancing power quality, custom power devices (CPDs) are recommended, among which the Dynamic Voltage Restorer (DVR) is considered the best and cost-effective solution. DVR is a power electronic-based solution to mitigate and compensate for voltage sags. This paper provides a thorough discussion and comprehensive review of DVR topologies based on operations, power converters, control methods, and applications. The review compares the state-of-the-art in works of literature, and comparative study on power quality issues, the DVR principle along with its operation modes, the DVR components, the DVR topologies based on energy storage, the DVR topologies based on single-/three-phase power converters, and the DVR topologies based on control units that have different control processing stages. Furthermore, modified and improved configurations of the DVR, as well as its integration with distributed generations, are described. This work serves as a comprehensive and useful reference for those who have an interest in researching DVRs.
Graphical Abstract
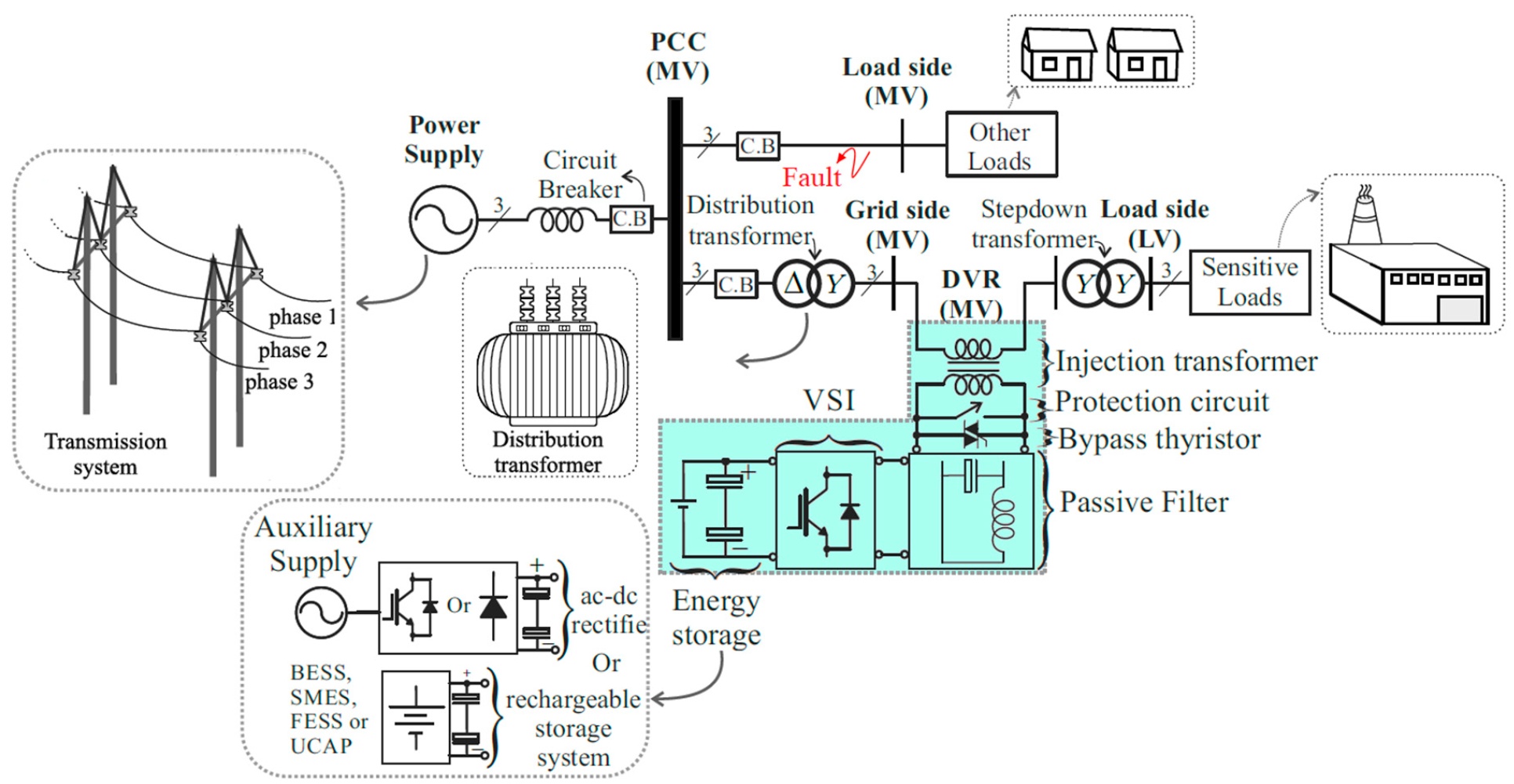
- A. Moghassemi, M. Hosseini, J. Olamaei, “Power Quality Improvement of Grid-Connected Photovoltaic Systems Using Trans-Z-Source Inverter Under Partial Shading Condition,” Iranian Journal of Science and Technology, Transactions of Electrical Engineering, vol. 44, no. 4, pp. 1429–1447, 2020.
doi 🔗Abstract
Voltage-source inverters have been widely used in traditional photovoltaic systems, which have limitations. To overcome, the Z-source inverter has been introduced. In spite of all the features introduced in the Z-source inverter, its configuration has been improved over the years, like the trans-Z-source inverter, which has added advantages compared to traditional inverters, namely, buck–boost feature, fewer passive elements, and a higher voltage boost gain. In this paper, photovoltaic arrays are connected to the grid via the trans-Z-source inverter with the aim of improving its power quality. Moreover, the shoot-through duty ratio is kept constant in the switching control method to add features like lower voltage stress (higher reliability), lower total harmonic distortion (lower maintenance cost), and higher voltage boost ratio. To evaluate the precision of the proposed system, the photovoltaic system is simulated on a standard grid and under partial shading conditions which bring about voltage sag, and hence, a dynamic voltage restorer is used to mitigate voltage sag. Simulation results are presented to verify the validation of the proposed photovoltaic system in terms of voltage and current THD, reducing 78.2% and 19.7%, respectively.
Graphical Abstract
- A. Moghassemi, S. Ebrahimi, J. Olamaei, “Maximum Power Point Tracking Methods Used in Photovoltaic Systems: A Review,” Signal Processing and Renewable Energy, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 19–39, 2020.
doi 🔗Abstract
This paper reviews and compares the most important maximum power point tracking (MPPT) techniques used in photovoltaic systems. There is an abundance of techniques to enhance the efficiency of photovoltaic systems. The crucial distinctions between these techniques are digital or analog implementation, simplicity of the design, sensor requirements, convergence speed, stability, range of effectiveness, and costs. Thus, opting for a suitable algorithm is vital as it affects the electrical efficiency of the PV system and lowers the costs by lessening the number of solar panels needed to get the desired power. Moreover, the paper provided a summary of the most used MPPT algorithms.
Graphical Abstract
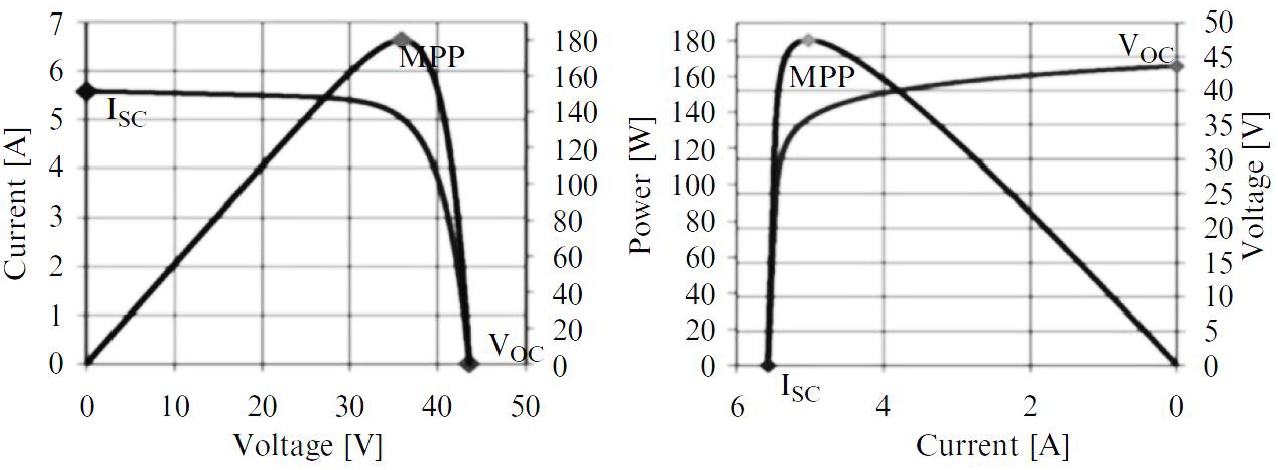
- A. Moghassemi, S. Ebrahimi, J. Olamaei, “MPPT and Current Mode Control Methods for PV Modules: A Review and A New Multi-Loop Integrated Method,” Signal Processing and Renewable Energy, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 1–22, 2020.
doi 🔗Abstract
This paper reviews various algorithms for the implementation of MPPT in a PV module integrated with a DC-DC converter and current mode control strategies for power converters. Also, a novel multi-loop integrated MPPT and current mode control for the Single-Ended Primary Inductance Converter (SEPIC) derived from the incremental conductance MPPT technique is proposed. A simulation model is developed using MATLAB/Simulink dynamic system simulation software to verify the operation of the control system developed in the paper. This ensures the efficient operation of the PV power plant by rapidly and accurately tracking the maximum power point (MPP) of the PV array. Moreover, the system is seen to offer robust voltage regulation and improved dynamic response in the face of changing environmental variables.
Graphical Abstract
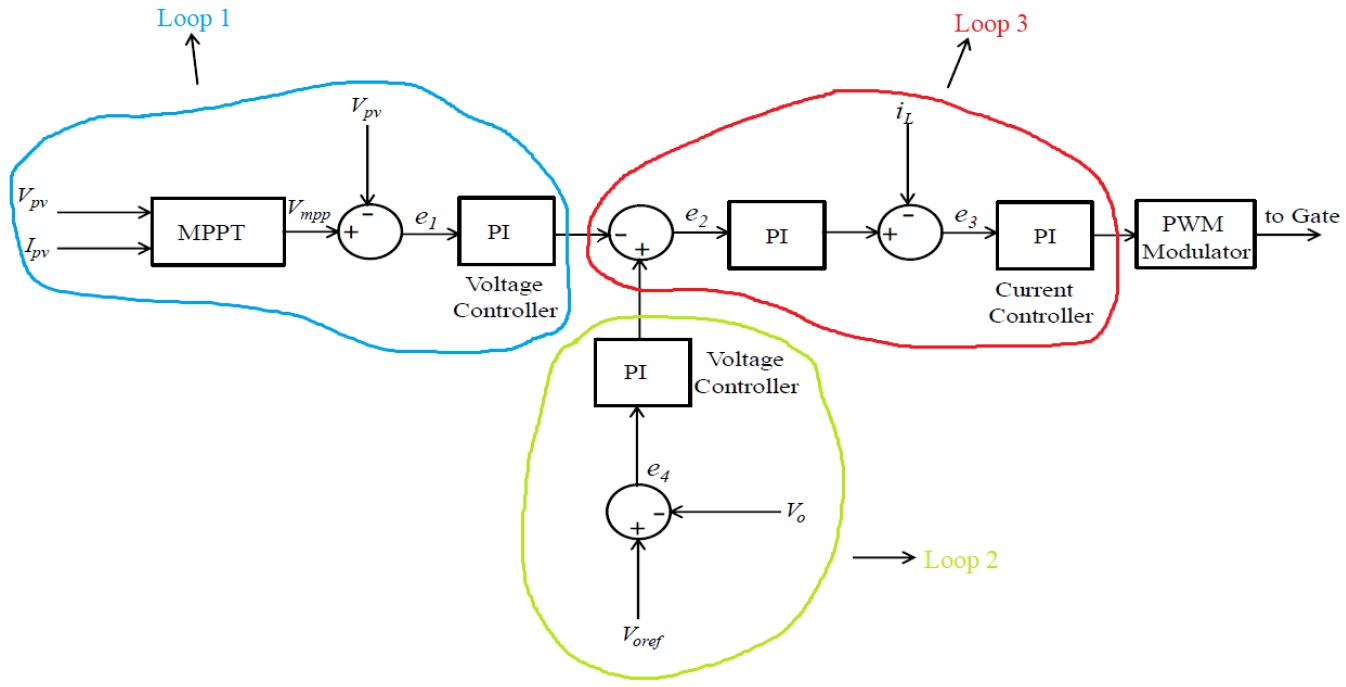
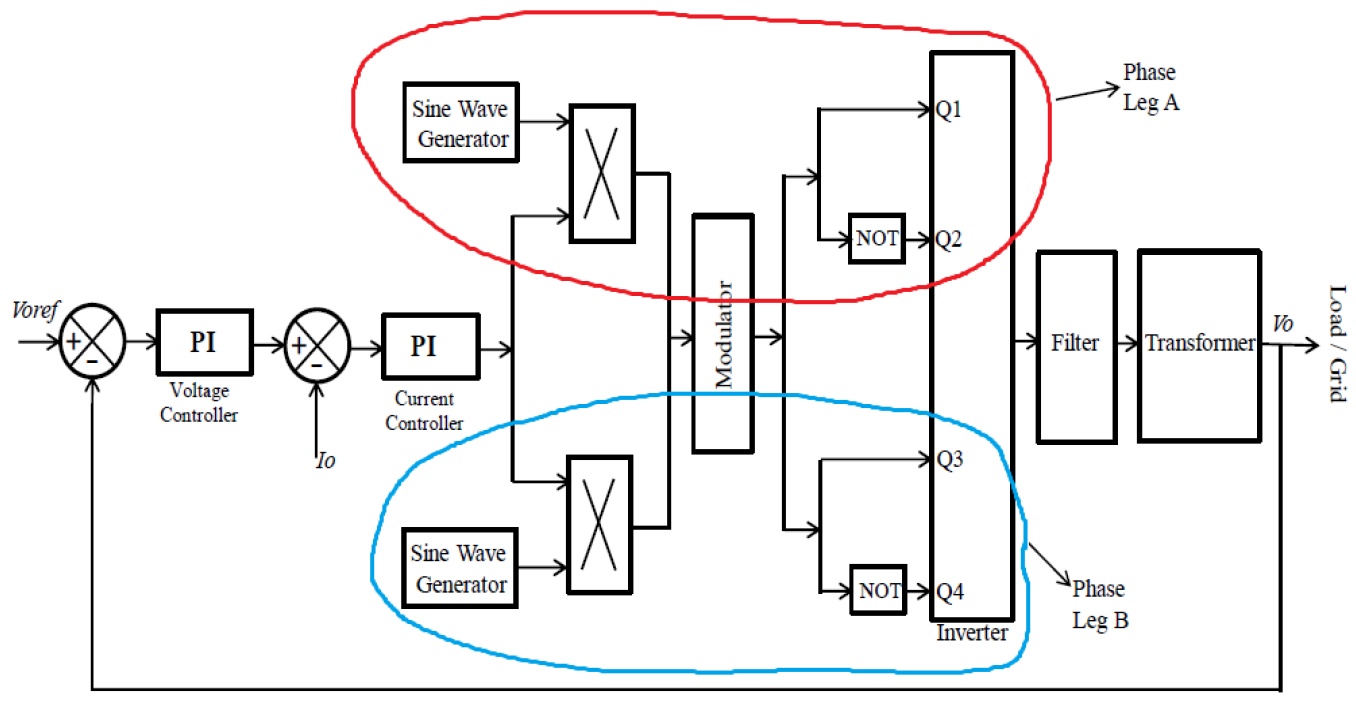
- S. Ebrahimi, A. Moghassemi, J. Olamaei, “PV Inverters and Modulation Strategies: A Review and A Proposed Control Strategy for Frequency and Voltage Regulation,” Signal Processing and Renewable Energy, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 1–21, 2020.
doi 🔗Abstract
To ensure the reliable delivery of AC power to consumers from renewable energy sources, the photovoltaic inverter has to ensure that the frequency and magnitude of the generated AC voltage are within acceptable limits. This paper develops models and control strategies for the DC-AC converter to ensure that the sinusoidal waveform of the desired frequency and magnitude, generated for both single-phase and three-phase operations, depends on the robustness of the inverter control system. The paper reviews various topologies and modulation approaches for photovoltaic inverters, operating in both single-phase and three-phase modes. Finally, a proposed control strategy is presented to ensure frequency and voltage regulation.
Graphical Abstract
2016
- J. Olamaei, S. Ebrahimi, A. Moghassemi, “Compensation of Voltage Sag Caused by Partial Shading in Grid-Connected PV System Through the Three-Level SVM Inverter,” Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments, vol. 18, pp. 107–118, 2016.
doi 🔗Abstract
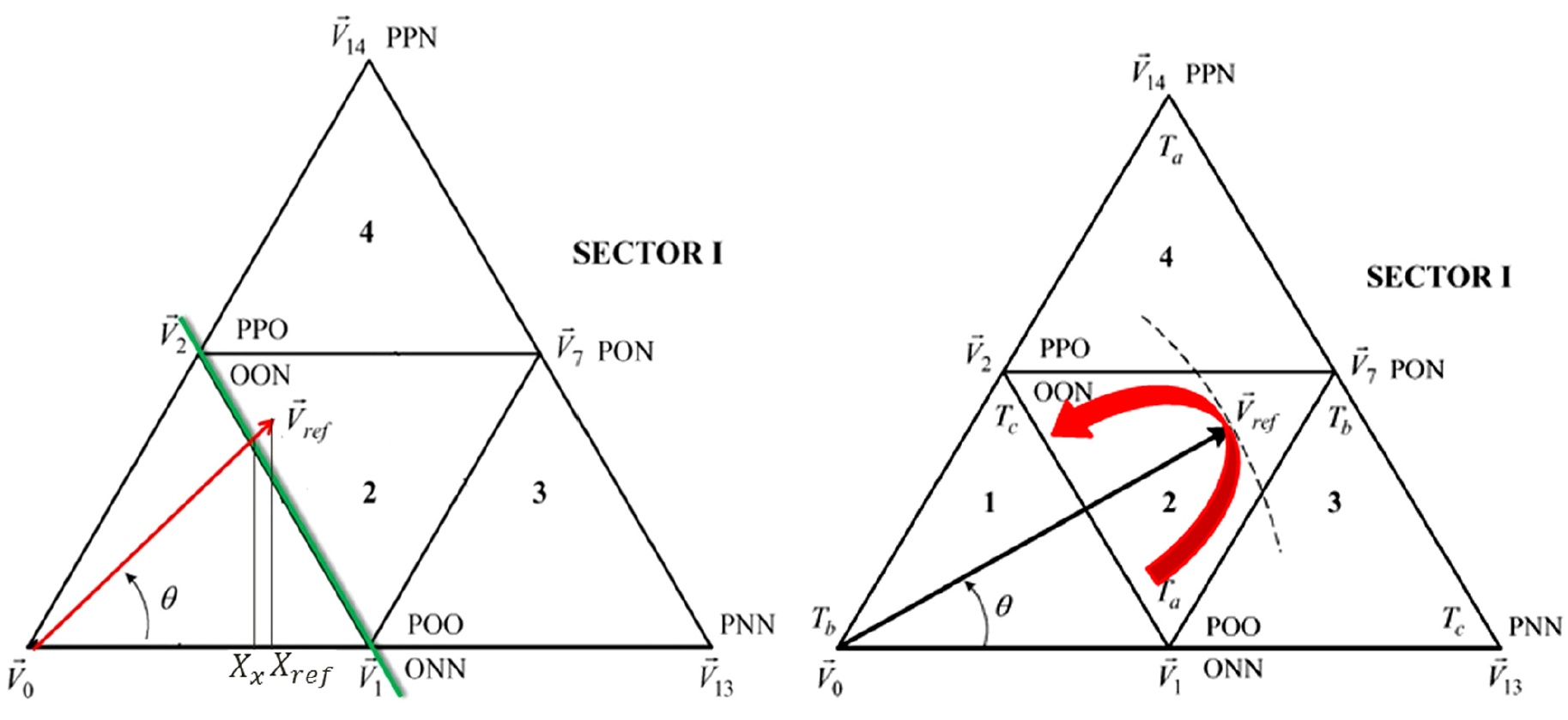
This study aims to evaluate the grid-connected PV system in partial shading conditions through the three-level SVM inverter and compensation of inverter output voltage sag caused by the partial shading using the dynamic voltage restorer (DVR). A function per time and the amount of radiation have been used to create the partial shading condition in the photovoltaic system. The advantages of the three-level SVM inverter include the complete region detection method, even in the boundary points between two regions, through boundary lines equations, and a complete online solution of those equations. Also, the reduction of total harmonic distortion (THD) through the switching table is appropriate. The results show that in the partial shading conditions, the three-level SVM inverter decreased THD in the presence or absence of DVR. DVR also compensates for the voltage sag to a suitable level. MATLAB/Simulink-based simulation results are presented for validation of the entire system.
Graphical Abstract
Conference Papers
2025
- A. Moghassemi, L. Timilsina, I. Rahman, G. Ozkan, B. Papari, C. Edrington, Z. Zhang, “Electro Thermal Management and Degradation Forecasting of Power Electronics Building Blocks in All-Electric Ships,” 2025 IEEE Electric Ship Technologies Symposium (ESTS), Old Town Alexandria, VA, USA, pp. 87–94, 2025.
doi 🔗Abstract
The Power Electronics Building Block (PEBB) concept integrates fundamental components into modular units, scalable for All-Electric Ships (AESs) through Modular Multilevel Converters (MMCs). MMC-based PEBBs offer modularity, low switching losses, good voltage and current quantization, and high efficiency. However, switching frequency greatly impacts converter design, influencing size, cost, and component stress. Higher frequencies reduce reactive component size but increase thermal stress and degradation of power modules. This paper proposes a Finite-Control Set Model Predictive Control (FCSMPC) method for multi-objective electro-thermal management of PEBBs, integrating a Deep Neural Network (DNN)-based degradation forecasting model. Results demonstrate the method's ability to maintain power quality, regulate junction temperature, and provide accurate degradation forecasts, enhancing reliability and mitigating aging.
Graphical Abstract
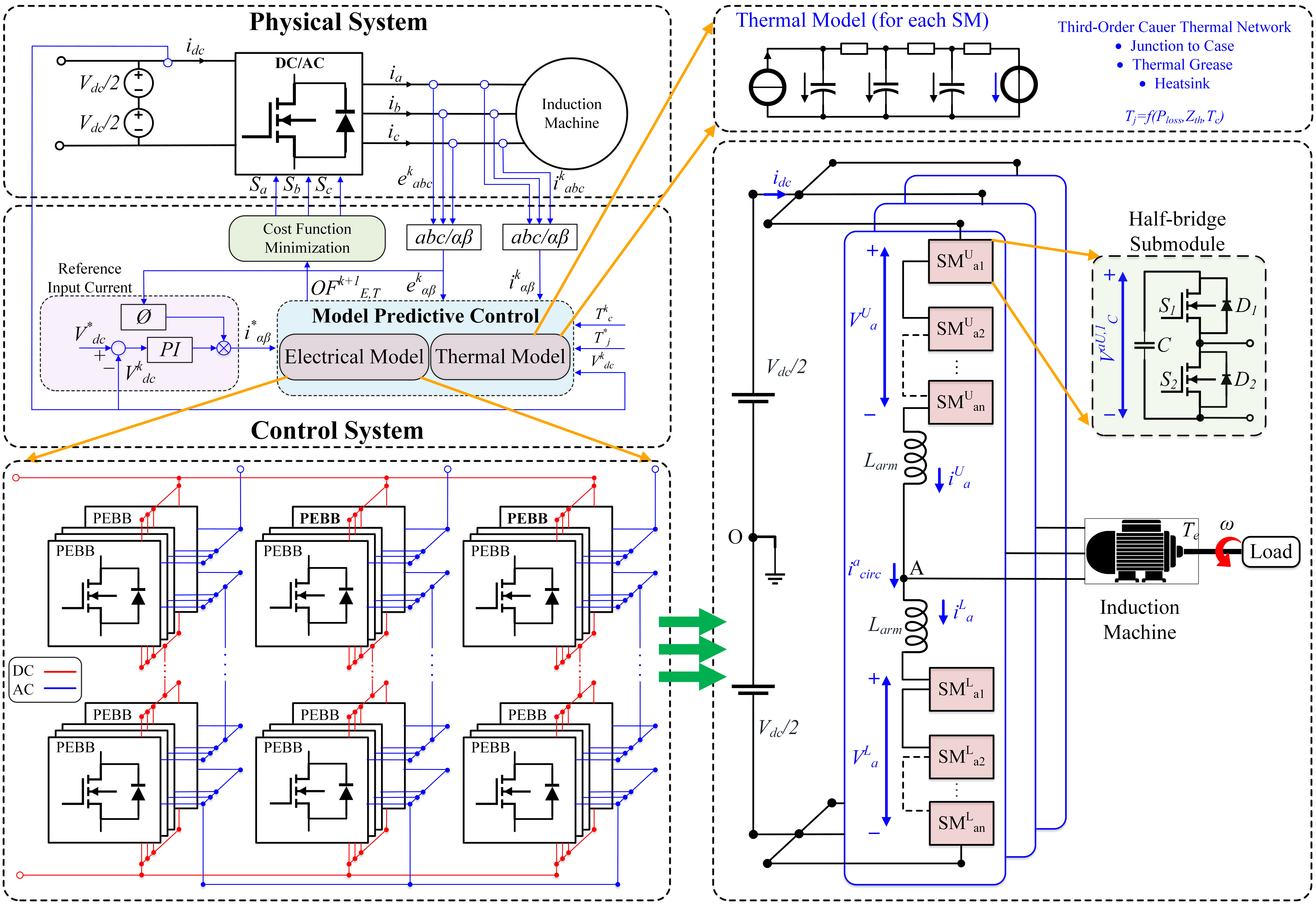
- I. Rahman, M. Ozden, A. Moghassemi, L. Timilsina, G. Ozkan, B. Papari, C. Edrington, “Power Routing Based Electro-Thermal Management of Parallel Power Electronic Converters in All-Electric Ships,” 2025 IEEE Electric Ship Technologies Symposium (ESTS), Old Town Alexandria, VA, USA, pp. 154–161, 2025.
doi 🔗Abstract
The application of power electronics in all-electric ships (AES) has grown significantly because they offer better control and flexibility. Additionally, Induction Motors (IM) are favored in AESs for their reliability, cost-effectiveness and superior speed and torque tracking performance. The reliability of the power converters in AESs is essential for their safe operation, and this is driving interest in new technologies that ensure safe and reliable PEC performance. One major challenge in achieving reliable PEC operation is the efficient management of generated heat. This includes control of junction temperature and regulation of thermal cycles in power semiconductors. Active Thermal Control (ATC) reduces high junction temperature and thermal cycles by using temperature-related control parameters. This paper presents a closed-loop ATC approach via power routing of parallel DC-AC converters that efficiently distributes the thermal load across various segments of a modular converter, thereby minimizing thermal stress on the most vulnerable components. The effectiveness of the proposed thermal management approach is validated through MATLAB/Simulink results.
Graphical Abstract
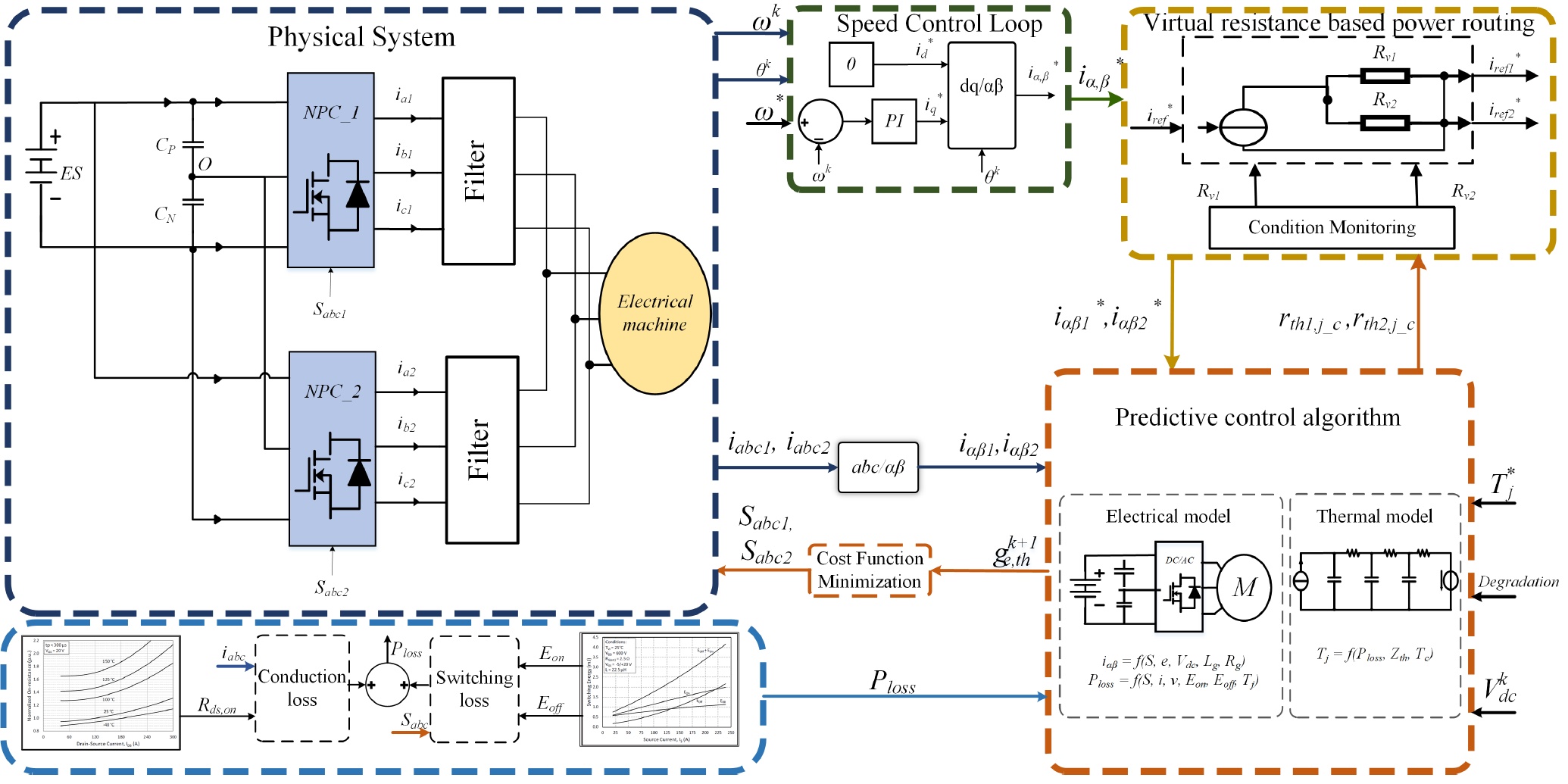
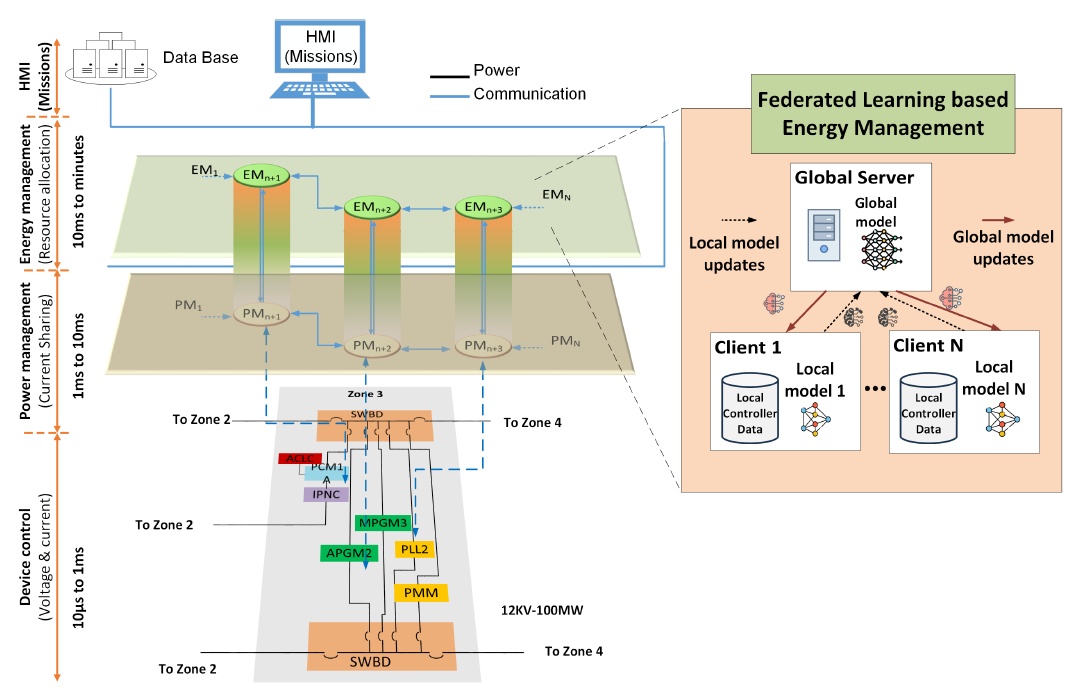
- A.A. Khan, G. Muriithi, L. Timilsina, A. Moghassemi, B. Papari, C. Edrington, G. Ozkan, N. Boghrabadi, Z. Wang, “Secure Energy Management For Ship Power System Using Federated Learning,” 2025 IEEE Electric Ship Technologies Symposium (ESTS), Old Town Alexandria, VA, USA, pp. 517–524, 2025.
doi 🔗Abstract
This paper presents a Federated Learning (FL) based Energy Management System (EMS) for Ship Power Systems (SPS). The proposed method addresses the challenges of maintaining a stable power supply while ensuring data privacy, a critical concern in shipboard environments. The FL framework enables collaborative training of Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) models across multiple generators without sharing sensitive local data. The use of FL, along with mitigating some of the security concerns associated with centralized Machine Learning (ML) configurations, also reduces the computational requirements, making the overall framework more scalable. The system was trained using load data from a Medium Voltage DC (MVDC) SPS. The results demonstrate accurate power output prediction and effective load management, indicating the potential of the proposed approach to enhance energy efficiency and reliability in ship systems.
Graphical Abstract
2024
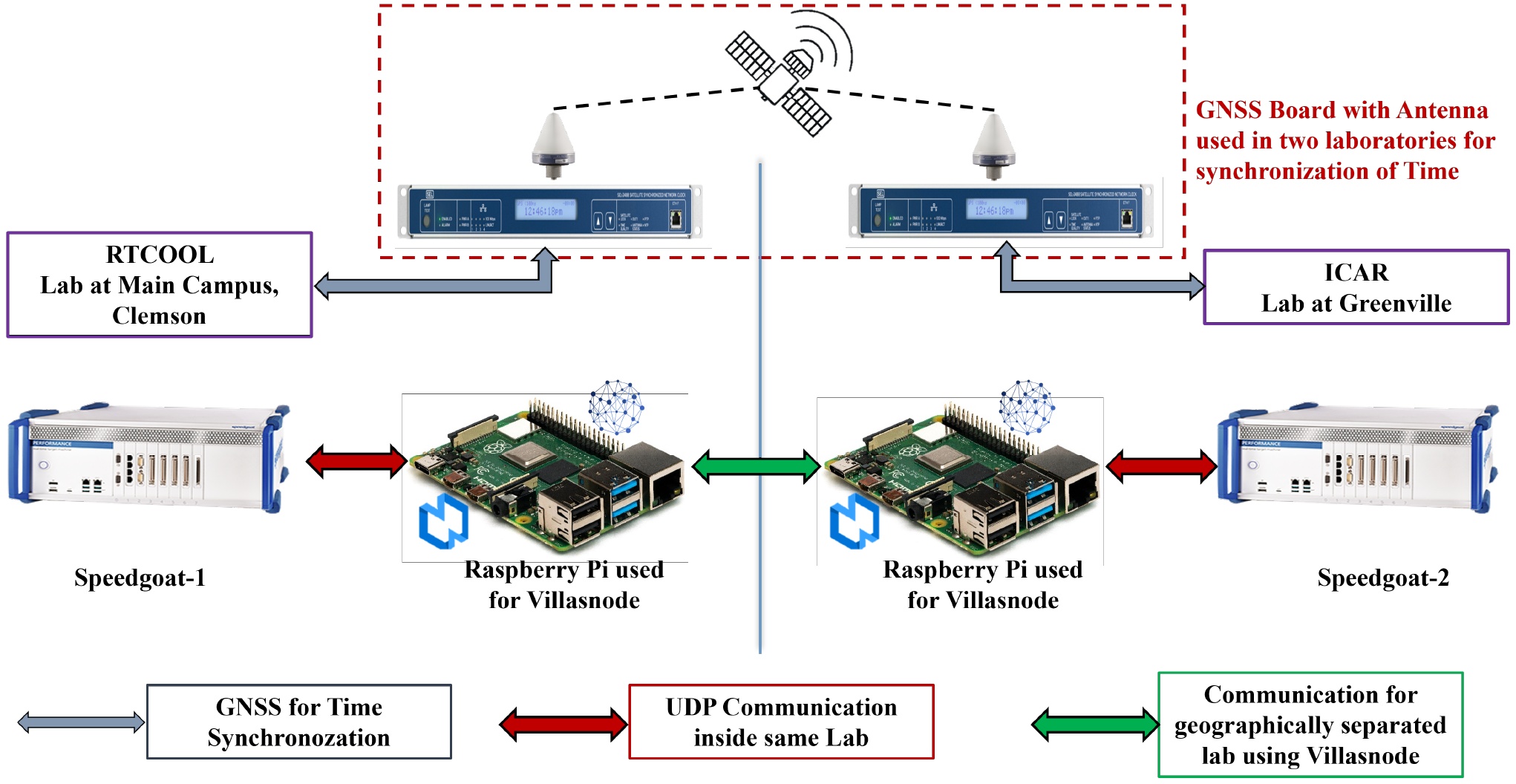
- L. Timilsina, E. Buraimoh, A. Moghassemi, I. Rahman, A. Arsalan, G. Muriithi, O. Ciftci, G. Ozkan, B. Papari, C. Edrington, “Hybrid Electric Vehicle Simulation Operation Across Distributed Laboratories Using Hardware Integrated Virtual Environment Concept,” 2024 IEEE 9th Southern Power Electronics Conference (SPEC), Brisbane, Australia, pp. 1–8, 2024.
doi 🔗Abstract
The research on hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) poses significant cost challenges due to the necessity of assembling various components and ensuring the fidelity of the entire system, especially when testing new algorithms or integrating additional devices. In research institutes, different laboratories may specialize in hardware or control aspects of HEVs, with some possessing most components while others lack certain elements. This fragmented distribution often necessitates purchasing all components, increasing research expenses substantially. To address this issue, this paper presents a framework introducing the concept of a hardware-integrated virtual environment (HIVE) that facilitates the virtual connection of components dispersed across multiple locations, enabling comprehensive research on the entire vehicle system without physical integration. To test this framework, this study utilizes a series HEV model developed in MATLAB, which is operated in real-time using Speedgoat, a digital real-time simulator. One laboratory possesses all the vehicle components except for the battery, while another laboratory houses the missing battery component, also developed in MATLAB and operated in real-time using Speedgoat. This study successfully establishes connectivity between the two laboratories, enabling the seamless operation of the entire HEV model across distributed locations.
Graphical Abstract
- A. Moghassemi, L. Timilsina, D. Scruggs, A. Arsalan, I. Rahman, A.A. Khan, O. Ciftci, B. Papari, G. Ozkan, C. Edrington, “Heuristic Evolutionary Optimization For Control and Management of Renewable-Based Hybrid Microgrids,” 2024 IEEE Sixth International Conference on DC Microgrids (ICDCM), Columbia, SC, USA, pp. 1–8, 2024.
doi 🔗Abstract
The surge in renewable energy and distributed generation necessitates advanced control systems for network performance enhancement. However, the lack of a standardized evaluation framework hampers comparisons, especially in complex hybrid networks. Hybrid energy systems offer greener and more reliable networks but require sophisticated control methods. To address this challenge, research explores novel linear and nonlinear techniques. This overview focuses on heuristic evolutionary optimization methods for Microgrids, covering AC, DC, and hybrid AC-DC systems, highlighting current research and future control requirements.
Graphical Abstract
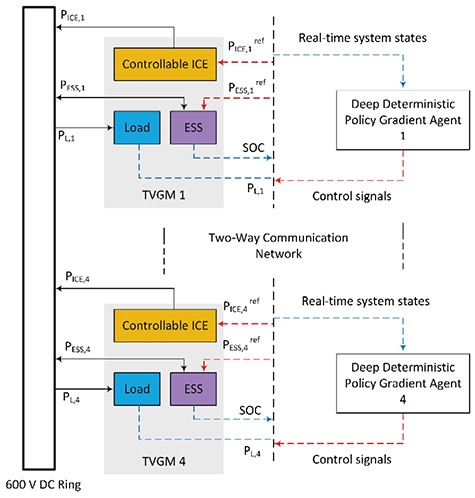
- E. Buraimoh, G. Ozkan, L. Timilsina, G. Muriithi, A. Arsalan, B. Papari, A. Moghassemi, C. Edrington, M. Ozden, “Distributed Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient Agents For Real-Time Energy Management of DC Microgrid,” 2024 IEEE Sixth International Conference on DC Microgrids (ICDCM), Columbia, SC, USA, pp. 1–5, 2024.
doi 🔗Abstract
This paper presents a real-world military use of a microgrid with Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) and Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V). This plug-and-play system delivers efficient, fast-deploying power for a contingency base within 20 minutes, generating up to 500 kW of three-phase power. It utilizes vehicle-based Internal Combustion (IC) engine generators and an Energy Storage System (ESS) to power vehicle equipment and off-board loads like shelters and communication centers. However, fluctuating off-board loads create operational challenges for this V2G-V2V microgrid. This work proposes a real-time implementation of energy management based on distributed Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG), a deep reinforcement learning, to address this problem for continuous state and continuous action spaces. This work formulates the energy management problem as a Markov decision process, considering random load demands and fuel costs. This paper aims to minimize the microgrid's operating costs by optimizing the dispatch of onboard vehicle power generators and storage units. With simulation experiments, this work demonstrates the effectiveness of the proposed distributed deep reinforcement learning approach. The results show the distributed DDPG agents can utilize the state of the ESS and significantly decrease the microgrid's overall operation costs. This validates the practical value of distributed DDPG for economic operations in military microgrids.
Graphical Abstract
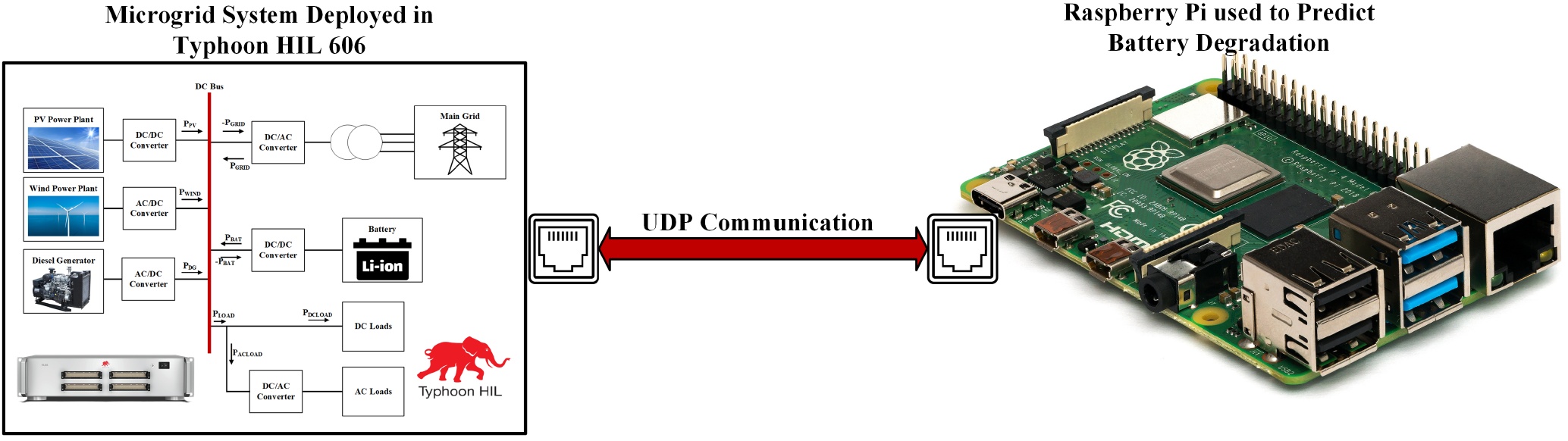
- L. Timilsina, A. Moghassemi, E. Buraimoh, I. Rahman, A.A. Khan, G. Muriithi, G. Ozkan, B. Papari, C. Edrington, “Degradation and State of Health Prediction of a Battery Used in a Microgrid in Real-Time,” 2024 IEEE Sixth International Conference on DC Microgrids (ICDCM), Columbia, SC, USA, pp. 1–7, 2024.
doi 🔗Abstract
Battery degradation is a complex physicochemical phenomenon intricately influenced by operational parameters and environmental factors. This paper delves into the degradation of lithium-ion batteries within microgrid systems, utilizing historical aging data from the University of Wisconsin-Madison to train a degradation model employing neural networks. The dataset is transformed to align with the battery pack rating pertinent to this investigation. The study identifies and examines several contributing factors to battery degradation, with a specific focus on temperature, charging current, discharging current, and depth of discharge. Emphasizing the significance of these parameters, particularly the latter three, the research endeavors to predict battery degradation in diverse operational conditions within a Microgrid system. This study modeled a Microgrid configuration capable of operating in islanded and grid-connected modes featuring solar PV, wind, a diesel generator, and a battery. Real-time simulations of different operational scenarios are conducted using the digital real-time simulator. Additionally, the battery's operational status is sent to a controller to predict its degradation and state of health. The controller used here is a Raspberry Pi, and communication is facilitated through the UDP protocol.
Graphical Abstract
- A. Moghassemi, L. Timilsina, I. Rahman, A. Arsalan, P.K. Chamarthi, G. Ozkan, B. Papari, C. Edrington, Z. Zhang, “Nearest Level Control Based Modular Multi-Level Converters for Power Electronics Building Blocks Concept in Electric Ship System,” 2024 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), Chicago, IL, USA, pp. 1–6, 2024.
doi 🔗Abstract
Power electronics building blocks (PEBBs) involve the integration of fundamental components into blocks with defined functionality, stacked in series and parallel, to extend converter power ratings to meet naval ship systems’ various power conversion needs. The PEBBs concept in literature is based on modular multilevel converters (MMCs). MMCs are promising candidates for medium and high-power system applications owing to their unique features, such as modularity/scalability/simplicity in structure, low switching losses, low quantization on voltage/current, high reliability, and high efficiency. However, a promising switching control method is required in MMCs to balance the capacitor voltage and suppress the circulating current. This paper presents the nearest level control (NLC) method for the PEBBs concept in modern electric ship systems to simultaneously improve capacitor voltage balancing, circulating current, and power quality. The simulation is conducted in MATLAB/Simulink software. A three-phase five-level MMC converter is considered for the simulation to analyze and compare the converter’s performance based on the proposed NLC and traditional sinusoidal pulse-width modulation (SPWM) switching methods.
Graphical Abstract
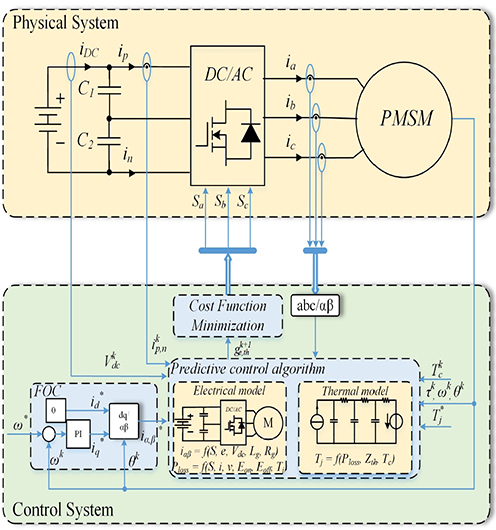
- I. Rahman, A. Moghassemi, L. Timilsina, P. Badr, Q. Zhu, R. Prucka, G. Ozkan, C. Edrington, “Model-Based Active Thermal Management for Neutral-Point Clamped Power Converter with Adaptive Weight,” 2024 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), Chicago, IL, USA, pp. 1–6, 2024.
doi 🔗Abstract
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines (PMSM) are commonly used for Electric Vehicles (EV) to benefit from their higher torque and efficiency, better performance, and heat dissipation capability than an asynchronous machine. The reliability of the power converters of PMSM drives is crucial for EV operation and is mainly related to the junction temperature of semiconductor devices. During operation, semiconductors experience periodic heating and cooling processes, which causes thermal stress. This stress causes failures of the devices and increases maintenance costs. This paper uses the Finite Control Set Model Predictive Control (FCS-MPC) approach to provide active thermal management (ATM) for a motor drive system. Active thermal management is a method to reduce the thermal cycling of the semiconductor device in order to improve the reliability of the motor drive system. The proposed method uses the FCS-MPC method to predict the three-level Neutral-Point Clamped (3L-NPC) converter’s electro-thermal characteristic to find its optimum state. The speed reference is converted to the reference current via Field-Oriented Control (FOC), and a Cauer-thermal network is used to predict the junction temperature of the semiconductors. The mission objectives vary during the EV operation; thus, adaptive weighting is applied to the objective function to control thermal cycling effectively. The preliminary results of the proposed method show that thermal cycling can be managed to improve reliability, and FCS-MPC is a powerful tool to provide multi-objective control for EV powertrains.
Graphical Abstract
- P.K. Chamarthi, A. Moghassemi, I. Rahman, L. Timilsina, O. Ciftci, E. Buraimoh, G. Ozkan, B. Papari, C. Edrington, “A Novel Four Switch Transformerless Inverter with Step Up/Down Capability for PV Fed Grid Connected Systems,” 2024 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), Chicago, IL, USA, pp. 1–5, 2024.
doi 🔗Abstract
This paper presents a novel four-switch transformerless inverter (FSTI) topology for 1-ø grid-connected solar photovoltaic applications with reactive power capability. This proposed FSTI steps up/down the output voltage while completely suppressing the leakage/parasitic currents. Further, this inverter topology supports the on/off-grid application where active/reactive power requirement is essential. In addition, the FSTI comprises of least active power devices, lower voltage and current stresses of power devices, appropriate THD in grid current and better efficiency. The FSTI performance is evaluated for the 1-ø grid connected system. The FSTI is modeled using small signal analysis for the grid-connected inverter's stable operation and fast response. The FSTI is validated on a 500VA laboratory prototype for input PV voltages of 100V, 180V and grid voltage of 110Vrms. The experimental results are in good agreement with the theoretical analysis, which verifies the practicality of the proposed inverter. The FSTI demonstrates the DC to AC power transfer while stepping up/down the inverter’s output voltage with maximum efficiencies of 97% and 96% for the input voltages of 180V and 100V, respectively.
Graphical Abstract

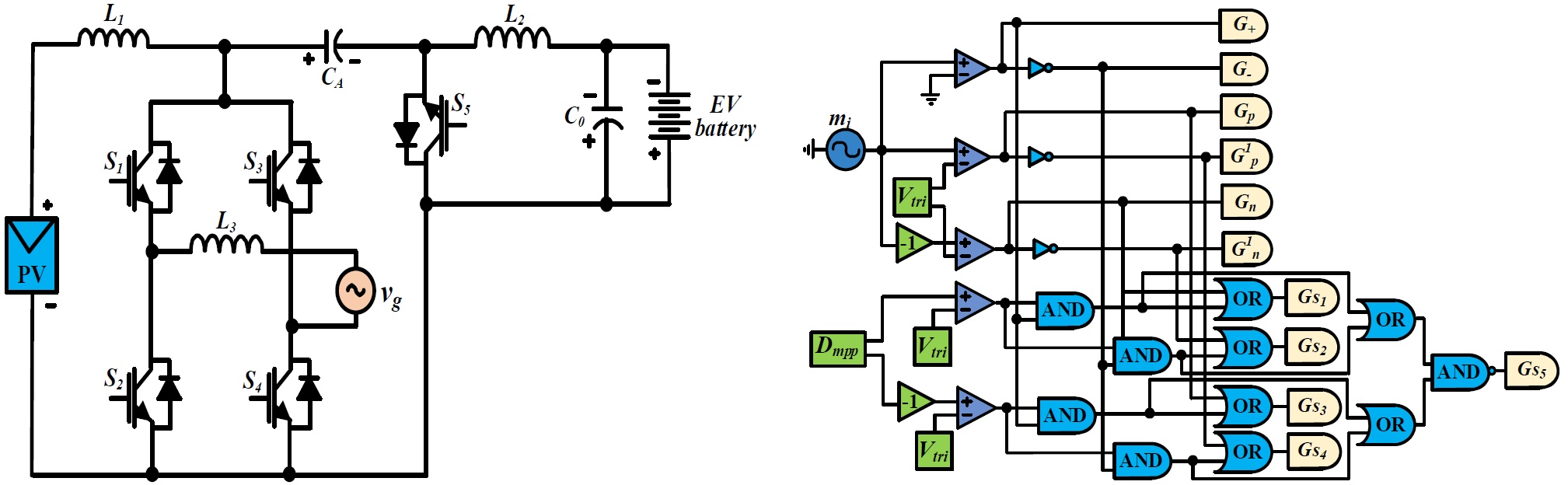
- P.K. Chamarthi, I. Rahman, A. Moghassemi, L. Timilsina, O. Ciftci, B. Papari, G. Ozkan, C. Edrington, “A Proposed Cuk Converter Based Dual Input Hybrid Converter Topology As EV Charging Station,” 2024 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), Chicago, IL, USA, pp. 1–6, 2024.
doi 🔗Abstract
The considerable advancement in electric vehicles (EVs) and constant reduction of prices for solar photovoltaic (PV) modules has raised interest in integrating PV modules to the EV chargers. In this paper a new Cuk based hybrid converter topology (CHCT) is proposed as an EV charger. The proposed CHCT consists of a PV source and 1-ϕ AC grid as two main energy sources. The main advantage of CHCT configuration is that it uses the optimal number of power components (i.e., five power switches, three inductors and one auxiliary capacitor) in the system. To control the CHCT configuration a simple modulation/switching strategy is proposed. Further, the control strategy to extract the maximum power available from PV source, controlling the power fed/extracted from the AC grid and charging the EV battery are also presented. In addition, the CHCT is tested under various scenarios such as the distribution of power between the two sources (AC grid and PV under wide variation of weather conditions), sending the power from PV to AC grid when EV battery is full or EV is not available, feeding power from PV to EV battery when AC grid is not available, and feeding power from AC grid to the EV battery during the absence of PV source. The MATLAB/Simulink is used to verify the proposed CHCT configuration under various circumstances at a power rating of 10kVA. The experimental testing of laboratory prototype of proposed EV charger is still under way. All the analysis and results of the proposed work will be presented in future papers.
Graphical Abstract
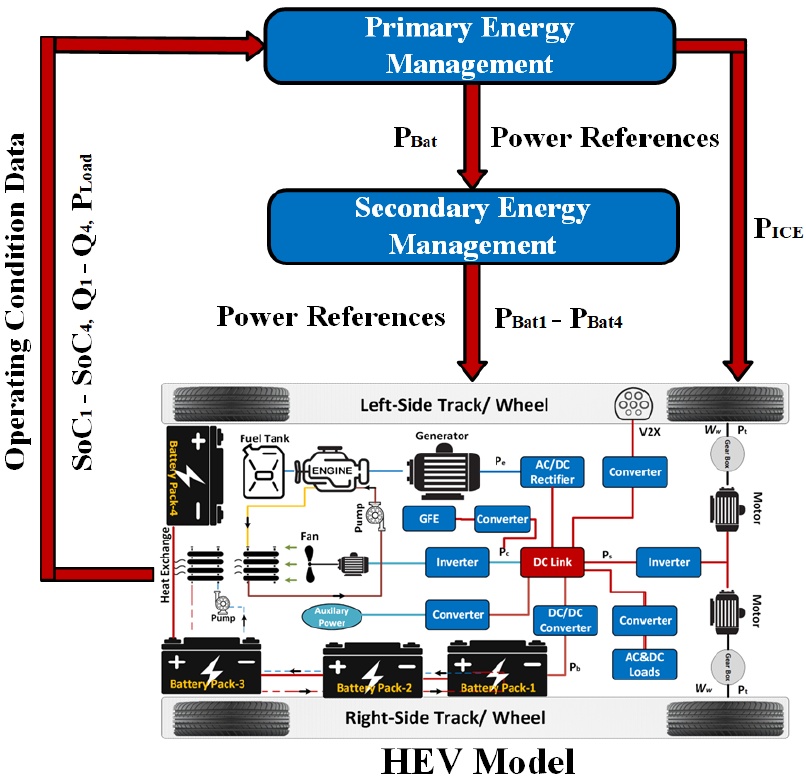
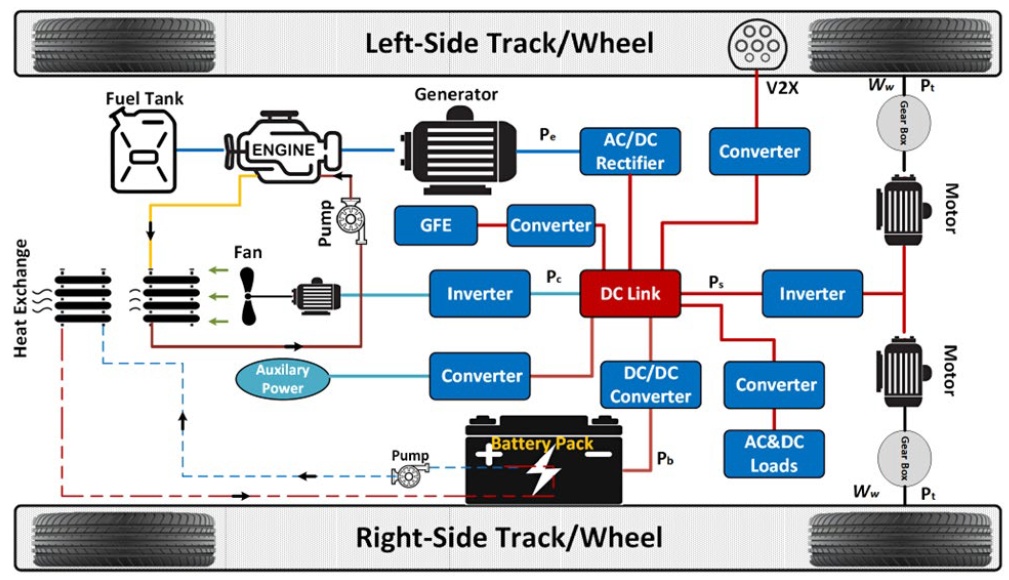
- L. Timilsina, O. Ciftci, A. Moghassemi, E. Buraimoh, I. Rahman, P.K. Chamarthi, G. Ozkan, B. Papari, C. Edrington, “A Dual Energy Management for Hybrid Electric Vehicles,” 2024 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), Chicago, IL, USA, pp. 1–6, 2024.
doi 🔗Abstract
Electric vehicles (EVs) are gaining increasing recognition as an effective means to combat climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Lithium-ion batteries have emerged as the prevailing choice for energy storage in the automotive industry, offering superior attributes to alternative battery technologies. In the context of EVs and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), the singular reliance on a single battery unit presents a challenge. Any fault within the battery impacts the vehicle's performance and raises concerns about its overall reliability. In an effort to enhance vehicle reliability, this paper introduces a novel approach that involves the use of multiple smaller battery packs to collectively match the capacity of a single, larger battery pack. Also, to effectively distribute power between the vehicle’s internal combustion engine and the various smaller battery packs utilized in the HEV configuration, this study proposes a dual energy management (EM) system. The first EM system allocates power between the engine and the battery packs with the primary objective of minimizing fuel costs. Meanwhile, the second EM system is responsible for distributing power among the different battery packs, aligning with the power requirements determined by the first EM system. To assess the viability and effectiveness of the proposed energy management solution, numerical simulations are conducted using MATLAB/Simulink. Two distinct scenarios are explored wherein the total capacity and the remaining capacity, often referred to as the State of Health (SoH), are varied for each of the smaller battery packs. Through these simulations, this paper aims to evaluate the practicality and performance of the designed energy management system under varying conditions.
Graphical Abstract
- L. Timilsina, A. Moghassemi, E. Buraimoh, A. Arsalan, P.K. Chamarthi, G. Ozkan, B. Papari, C. Edrington, “Impact of Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) on Battery Degradation in a Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle,” SAE World Congress Experience (SAE WCX), Detroit, MI, USA, 2024.
doi 🔗Abstract
Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming increasingly recognized as an effective solution in the battle against climate change and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Lithium-ion batteries have become the standard for energy storage in the automobile industry, widely used in EVs due to their superior characteristics compared to other batteries. The growing popularity of the Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) concept can be attributed to its surplus energy storage capacity, positive environmental impact, and the reliability and stability of the power grid. However, the increased utilization of the battery through these integrations can result in faster degradation and the need for replacement. As batteries are one of the most expensive components of EVs, the decision to deploy an EV in V2G operations may be uncertain due to the concerns of battery degradation from the owner’s perspective. This paper examines the degradation of the battery employed in Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) for both V2G connection and its typical operating schedule. For assessing the degradation in driving scenarios, the US06 drive cycle is employed. On the other hand, for the V2G scenario, a 10 kW bidirectional charger is utilized. The charger discharges the battery up to 20 kWh in 2 hours or up to 60% state of charge (SoC) and subsequently charges it back to 90% SoC at a constant 1C rate. This V2G setup simulates the discharging and charging patterns typically observed in real-world scenarios and allows for evaluating battery performance and degradation under such conditions. Finally, an economic analysis is conducted by considering the capacity loss of the battery resulting from the V2G connection. This study considers the incentives obtained through the V2G connection, providing an assessment of the economic viability and potential benefits associated with utilizing the vehicle in V2G applications.
Graphical Abstract
- A. Arsalan, B. Papari, I. Rahman, L. Timilsina, A. Moghassemi, G. Muriithi, G. Ozkan, C. Edrington, “Machine Learning Approach for Open Circuit Fault Detection and Localization in EV Motor Drive Systems,” SAE World Congress Experience (SAE WCX), Detroit, MI, USA, 2024.
doi 🔗Abstract
Semiconductor devices in electric vehicle (EV) motor drive systems are considered the most fragile components with a high occurrence rate for open circuit fault (OCF). Various signal-based and model-based methods with explicit mathematical models have been previously published for OCF diagnosis. However, this proposed work presents a model-free machine learning (ML) approach for a single-switch OCF detection and localization (DaL) for a two-level, three-phase inverter. Compared to already available ML models with complex feature extraction methods in the literature, a new and simple way to extract OCF feature data with sufficient classification accuracy is proposed. In this regard, the inherent property of active thermal management (ATM) based model predictive control (MPC) to quantify the conduction losses for each semiconductor device in a power converter is integrated with an ML network. This recurrent neural network (RNN)-based ML model as a multiclass classifier localizes the faulty switch based on the dynamics associated with conduction losses as reliable and feature-rich data. The presented approach utilizes the controller data with no additional computational load to compute the feed-in data for the ML model and no extra hardware requirements. The proposed data-driven approach, with an accuracy of 99% for distinct hyperparameters and testing datasets, proves to be a promising solution for OCF DaL.
Graphical Abstract
2023
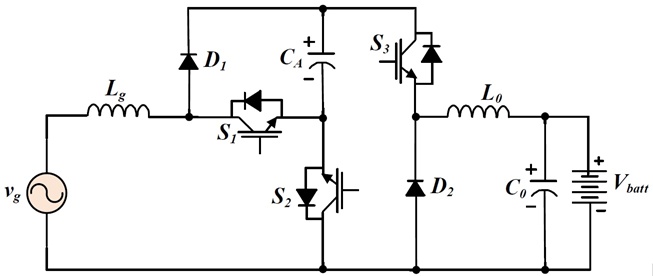
- P.K. Chamarthi, C. Edrington, A. Arsalan, L. Timilsina, B. Papari, G. Ozkan, A. Moghassemi, “A Novel 1-ϕ Cuk Based On-Board EV Charger with Minimal Power Components,” 2023 SAE Energy & Propulsion Conference & Exhibition (EPCE), Greenville, SC, USA, 2023-01-1686, 2023.
doi 🔗Abstract
This paper proposes a novel 1-ϕ, Cuk based on-board electric vehicle (EV) charger with least power components. The proposed EV charger has a special feature to achieve power factor correction (PFC) at AC grid without requirement of the grid voltage and current sensors which cuts the cost and increases the power density of the EV charger along with robustness to noise. The automatic PFC at AC grid is accomplished by operating the output DC inductor in discontinuous conduction mode (DCM). The proposed EV charger necessitates a minimal number of power components for positive and negative half cycles of AC grid which improves the overall efficiency of the system. This is possible due to the combination of inverting and non-inverting Cuk converters are used for each half cycle of the AC grid. Further, the presence of output inductor in the EV charger reduces the ripples in the output current which is not common with all the existing chargers in the literature. In addition, the control of charger is simple, and easy to implement with only battery current sensor based current control. The proposed charger configuration has lower voltage stress across the power switches and diodes in comparison with the existing charger configurations. The theoretical concept is validated through experimental studies which prove the superior execution of PFC control of the 2kW EV charger. The various performance factors such as power factor at AC grid is 0.996 and total harmonic distortion (THD) in the AC grid current is 2.8% which are within the limits of standard IEC 61000-3-2.
Graphical Abstract
- A. Moghassemi, G. Ozkan, C. Edrington, G. Muriithi, Z. Zhang, “Active Thermal Control of AC/DC Power Converter Considering Health Monitoring of Power Modules,” 2023 IEEE Electric Ship Technologies Symposium (ESTS), Old Town Alexandria, VA, USA, pp. 78–85, 2023.
doi 🔗Abstract
The evolution of power electronics devices in the semiconductor sector has created a strong need for power modules that have high efficiency and low power usage. The power package; which embraces a couple of power electronics devices such as switches and diodes; provides mechanical supports, electrical interface, protection, and thermal management to the power electronics devices. The power package is power dissipation, resulting in a significant challenge to its thermal management. To lower the expenses on wasted power and minimize the need for cooling systems, it is imperative for power converters and their control algorithm to offer exceptional efficiency in converting power. Hence, efficient thermal control and sophisticated thermal design are crucial in developing the power module. In this paper, health monitoring of the power modules is considered in the active thermal control of a two-level power rectifier using a sequence-based model predictive control method. This paper sets the stage for monitoring the thermal response and health of power electronics devices by early diagnosis of degradation. This declines the thermal stress and makes a prompt prediction of failure. This would enhance the reliability of the power converter.
Graphical Abstract

- G. Muriithi, B. Papari, A. Moghassemi, A. Arsalan, G. Ozkan, C. Edrington, “Security Enhancement of Cyber-Physical DC Ship Power System Using Scalable Deep Learning Method,” 2023 IEEE Electric Ship Technologies Symposium (ESTS), Old Town Alexandria, VA, USA, pp. 520–527, 2023.
doi 🔗Abstract
Cyber-physical systems like ship power systems are highly susceptible to cyber threats and physical faults. Early detection and mitigation of cyber-attacks using Machine Learning (ML) techniques are garnering more attention as cyber-physical attacks become more frequent and sophisticated. ML has demonstrated promising performances in developing robust threat intelligence solutions. In this paper, a cyber-attack detection scheme for the ship control system using a scalable federated deep learning-based method is proposed. Here, Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) models are trained in a distributed manner to mirror complex controller behavior using normal system operational data. Estimation errors between the actual controller data and the ML counterparts are used to detect the presence of cyberattacks or anomalous behavior. Additionally, temporal analysis is conducted on both the input and output estimation error signals whereby a time gap is detected that is leveraged to distinguish between hijacking and FDI attacks. Simulation results indicate that the proposed methods can effectively detect multiple types of cyberattacks instantly without sharing sensitive data.
Graphical Abstract
2021
- A. Moghassemi, S. Ebrahimi, F. Ferdowsi, “A Novel Control Scheme for TransZSI-DVR to Enhance Power Quality in Solar Integrated Networks,” 2021 North American Power Symposium (NAPS), College Station, TX, USA, pp. 1–6, 2021.
doi 🔗Abstract
This paper aims to study and evaluate the performance of a novel control scheme for Dynamic Voltage Restores (DVR) with Transformer-based Impedance Sourse Inverter (Trans-ZSI) configuration. An Improved Maximum Constant Boost Control (IMCBC) method is proposed to enhance the overall performance of solar PV fed TransZSI-DVRs. The proposed technique contributes to THD reduction and voltage stress mitigation across the switches. A model developed in Matlab/SIMULINK is tested under different types of voltage disturbance. The results show the effectiveness of the proposed control method as a corrective approach in compensating the voltage at the point of common coupling.
Graphical Abstract

2020
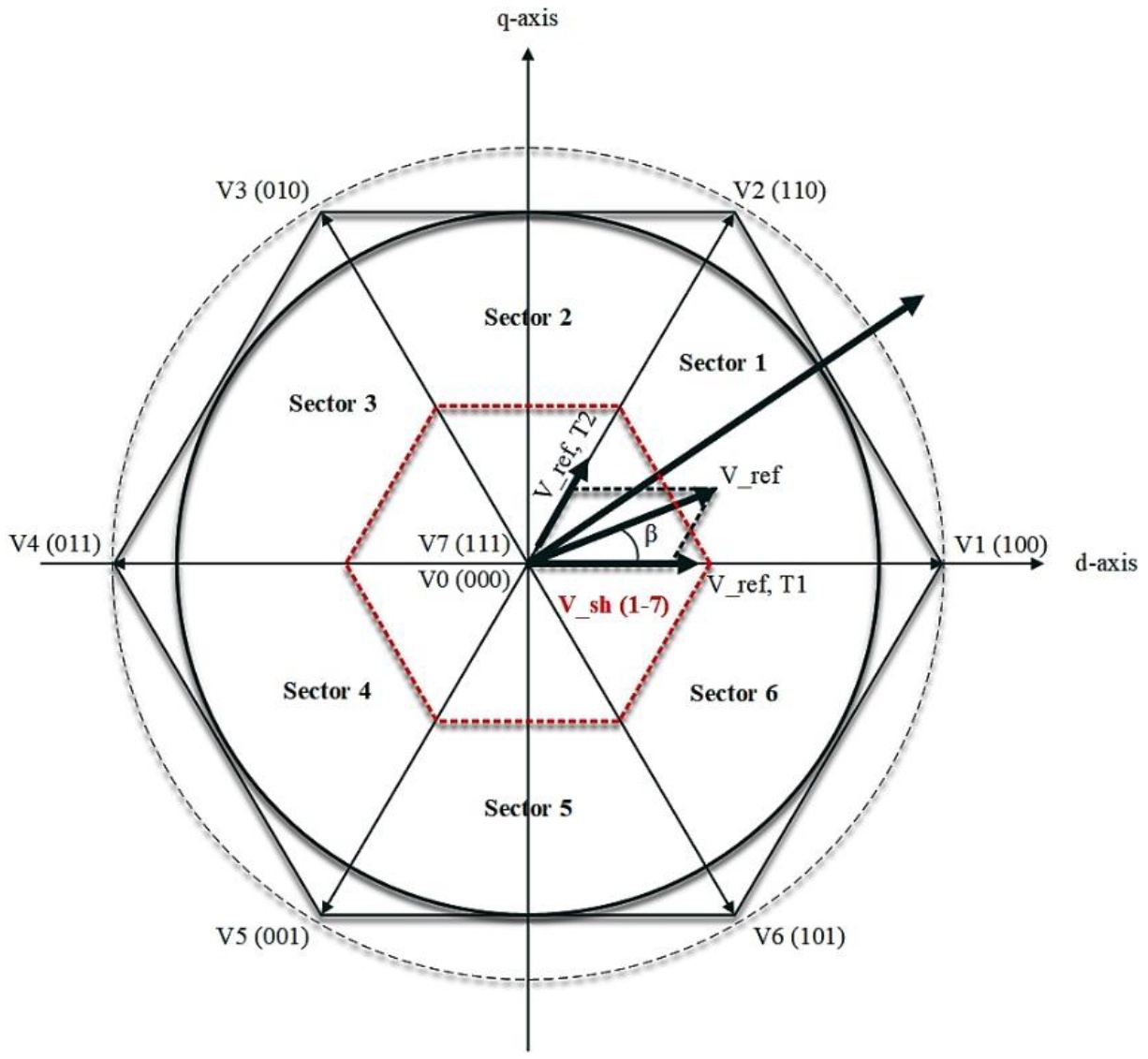
- A. Moghassemi, S. Ebrahimi, “Modified SVPWM for Trans-Z-Source Inverter-Based PV Systems,” The 7th National Congress of Electrical and Computer Engineering of Iran, Tehran, Iran, 2020.
doi 🔗Abstract
In this paper, a modified space vector PWM is presented for Trans-Z-source inverter -based grid -connected photovoltaic systems. In this method, the shoot-through states are added which bring outstanding merits like lower total harmonic distortion, lower voltage stress (higher reliability) and higher voltage boost gain, as opposed to traditional methods. Plus, the Trans- Z-source inverter has an ideal transformer and a capacitor, which can overcome limitations of traditional voltage-source inverters and z-source inverters. Buck/boost feature, fewer passive elements, and higher voltage boost gain are its advantages. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed switching method, the photovoltaic system is analyzed in three different cases: based on the voltage-source inverter with carrier-based PWM, based on the trans-z-source inverter with maximum constant boost control and based on the trans-z-source inverter with modified space vector PWM. Simulation results confirm the superiority of the proposed photovoltaic system with the modified space vector PWM in terms of the power quality and the voltage stress.
Graphical Abstract
- F. Zareei, M. Hosseini, A. Moghassemi, “Optimal Placement and Sizing of Distributed Generation via a Hybrid Multi-Objective Artificial Bee Colony and Differential Evolution Algorithms,” The 7th National Congress of Electrical and Computer Engineering of Iran, Tehran, Iran, 2020.
doi 🔗Abstract
Distributed generations (DG) are used in power systems to reduce power losses, improve voltage level, increase the reliability and reduction of environmental pollution. To use the advantages of DG units, optimal placement and sizing of these systems should be taken into account. In this paper Differential Evolution algorithm (DE) used as an algorithm capable in the field of artificial intelligence combined with the Artificial Bee Colony algorithm (ABC) to enhance search capabilities of the DE algorithm for placement and sizing of DG units in presence of load uncertainty in distributed power systems. To demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, it is tested on a standard IEEE-69 bus network and results indicate the superiority of the hybrid algorithm compared to each one of them. Besides, the uncertainty of loads is considered. Simulation results in MATLAB/Simulink software show that the proposed algorithm (DE-ABC algorithm) minimized total cost and power losses of DG units and voltage deviation has been improved.
Graphical Abstract
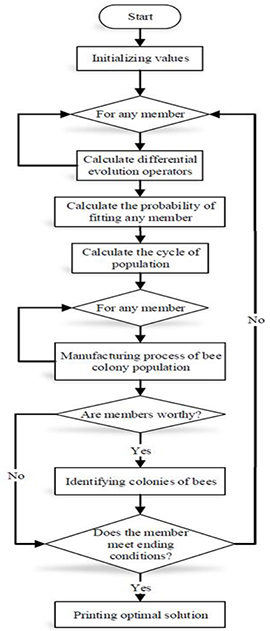
- S. Ebrahimi, A. Moghassemi, M. Mola, “Target Tracer Switching Strategy for Multi-Level PV Inverters Motor Drives Based on MPC,” The 7th National Congress of Electrical and Computer Engineering of Iran, Tehran, Iran, 2020.
doi 🔗Abstract
Implementing the Model Predictive Control (MPC) is much more popular due to the capability of controlling the linear and nonlinear loads without linearization as well as no need for a modulator to generate switching signals. The performance of MPC methods is basically related to their cost function to examine all possible voltage vectors generated by inverters to find the optimal one. This requires to consume lots of time which can become more at high-level inverters. In this paper, the proposed Target Tracer MPC (TT-MPC) switching strategy not only can lessen the loss caused by the high number of inverter switching commutation, but also there is no need to examine all voltage vectors to choose the optimal one. By finding and tracing simultaneously the stator voltage vector region, TT -MPC examines only the vectors of that sector and the two adjacent sectors. Therefore, its cost function requires a very short time comparing with other MPCs to find the optimal voltage vector. This advantage of TT-MPC can make it possible to have fast responding and precise control over four quadrants of the motor drive. This issue is way too much vital when it comes to PV inverters.
Graphical Abstract
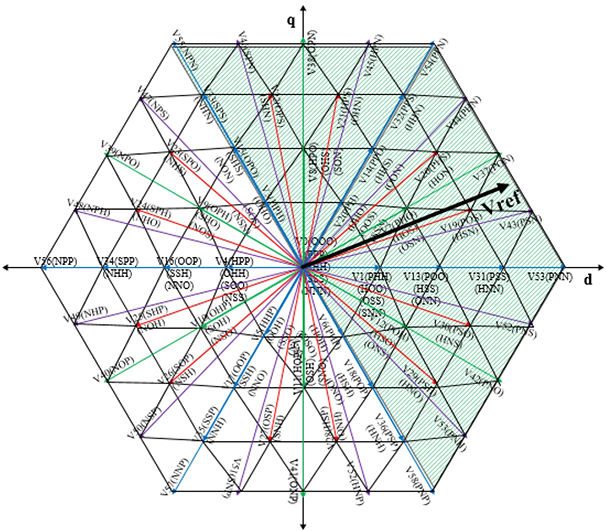
2014
- A. Moghassemi, J. Olamaei, M. Hosseini, “Simulation of Photovoltaic System Based on Zero-Current Switching Forward Converter,” The 17th Iranian Student Conference on Electrical Engineering, Kish, Iran, 2014.
doi 🔗Abstract
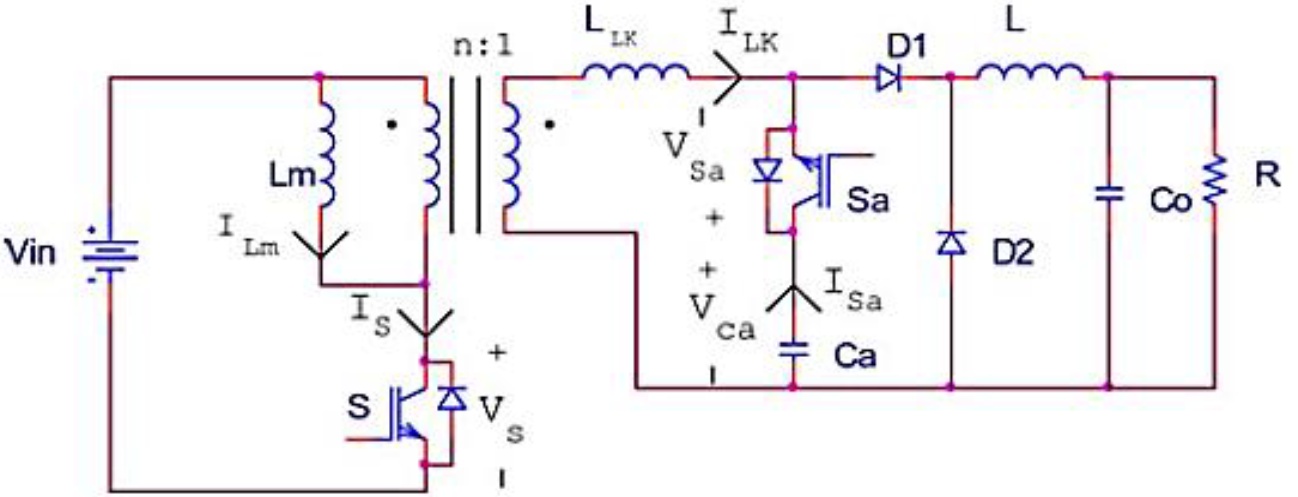
In this paper, with the help of a simple auxiliary circuit and a new algorithm for switching in a pulse width modulation forward converter, features of a Photovoltaic system and soft switching have been achieved. In this converter, the transformer core is reset via resonance, and as a result, reset winding is not required which is the main advantage of this converter over existing zero-current switching forward converters. Also, the proposed auxiliary circuit uses the leakage inductance of the transformer for the resonant inductor and does not require any additional inductor. Thus, the main and auxiliary switches are soft-switched. The simulation and the output characteristic of PV and switches are simulated in MATLAB Simulink.
Graphical Abstract
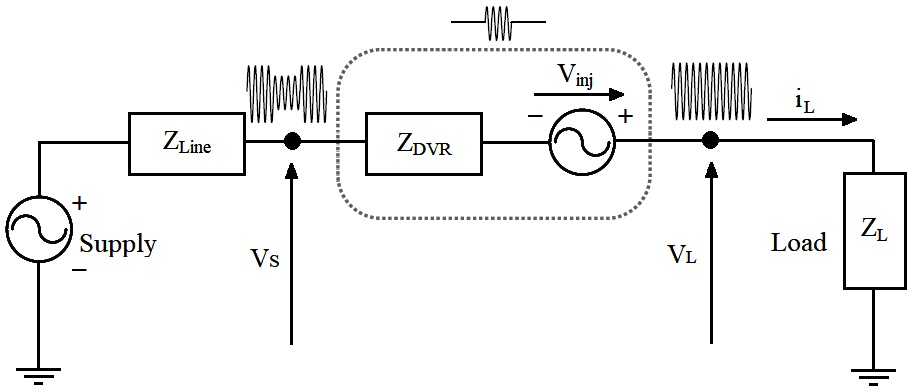
- A. Moghassemi, K. Rostampoor, “New Control Technique in DVR As A Series Compensator to Protect Sensitive Loads Against Voltage Disturbances,” The 1st Conference on Electrical and Electronic Engineering North West of Iran, Tabriz, Iran, pp. 76–81, 2014.
doi 🔗Abstract
In power systems, custom power devices are used to prevent voltage drop. Dynamic Voltage Restorer (DVR) is one of them. Also, there are different control techniques for DVR systems. The purpose of this paper is to use DVR with the dq0 control technique as a series compensator for the protection of sensitive and critical loads during faults, voltage sags, and voltage swells. The proposed control system has been simulated in MATLAB/Simulink software. The results show that the DVR system is useful for improving voltage disturbances.
Graphical Abstract
Book Chapters
2022
- T. Kerci, W. Zhong, A. Moghassemi, F. Milano, P. Moutis, “Frequency Control and Regulating Reserves by VPPs,” Scheduling and Operation of Virtual Power Plants, pp. 131–162, Cambridge: Elsevier, 2022
doi 🔗Abstract
The virtual power plant (VPP) is a paradigm that aggregates widely dispersed resources over an electrical grid or part of it thereof and aspires to emulate the behavior of conventional generators. In this sense, VPPs are expected to contribute to system services. One of the most typical and important system services is frequency control. Frequency control ensures the continuous balance of generation and demand and acts so to preserve it in real-time as imbalances occur. To realize this service, proper reserves, defined as regulating reserves, must be procured and retained to respond to any imbalance during a given planning time-frame. As VPPs comprise multiple different resources, which are dispersed over potentially vast areas, procuring regulating reserves and realizing frequency control is a challenging task. This chapter defines frequency control as a service offered by VPPs, and also illustrates the ways this service may be planned and realized.
Graphical Abstract
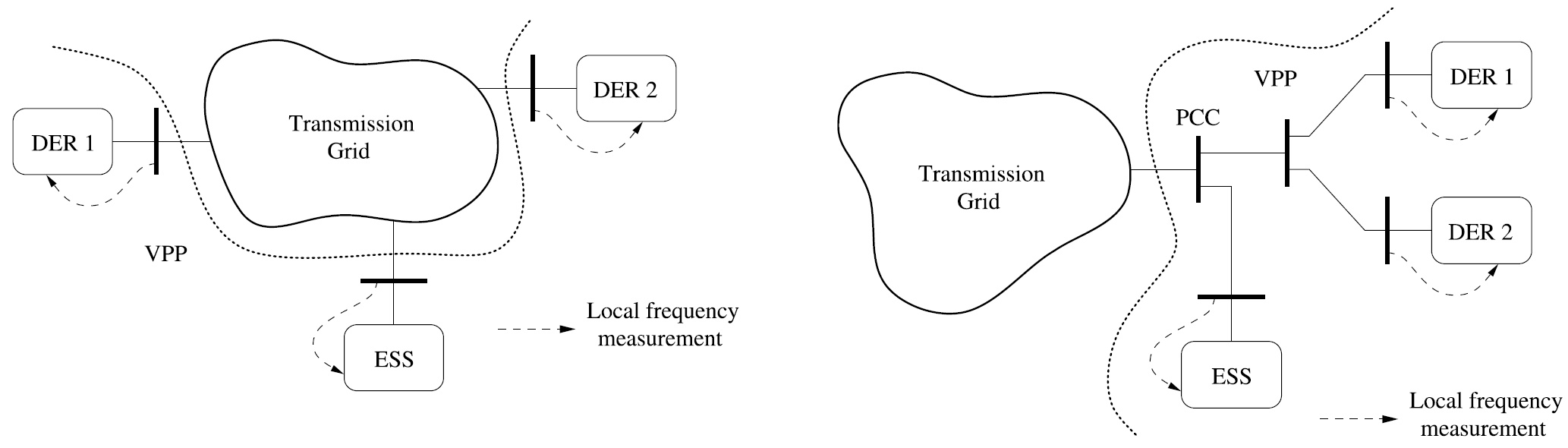
- P. Moutis, A. Moghassemi, “Frameworks of Considering RESs and Loads Uncertainties in VPP Decision-Making,” Scheduling and Operation of Virtual Power Plants, pp. 163–190, Cambridge: Elsevier, 2022.
doi 🔗Abstract
Uncertainties are inherent to most aspects of power system operation, including the load that the overall infrastructure aims to serve. It is critical to examine how and to what extent uncertainty affects virtual power plants (VPPs) and how VPPs handle it. In this chapter, we briefly discuss the sources of uncertainty that are more substantial to the operation of a VPP, how researchers have addressed, quantified, and controlled it, and what we consider to be the path forward. Briefly, it needs to be noted that the subject requires considerably more research with approaches that have been barely used and combinations of them thereof for more all-round handling of the issue.
Graphical Abstract

Books
2019
- A. Moghassemi, S. Ebrahimi, “Application of Renewable Energy Systems in MATLAB/Simulink Software: PV Solar and Wind Turbine,” Roham Andisheh Press, Tehran, Iran, 2019.
doi 🔗Abstract
MATLAB® is the high-level programming language developed for solving technical and mathematical problems. It is used widely not only in academic courses but also in scientific and engineering activities. The graphical programming language Simulink® is included in MATLAB. Simulink is used for simulating dynamical systems. It is supposed that the system under investigation is developed as a functional diagram consisting of blocks that are equivalent, by their functions, to the program blocks that are included in the Simulink library. This book is intended primarily for later year undergraduate, graduate and research students who are fascinated to learn how to model and control Renewable Energy Systems based on MATLAB/Simulink software. It starts with a comprehensive review of fundamental principles of codes, functions, structures, graphics and graphical user interface programming and then moves on to explain mathematical model of Renewable Energy Systems, PV solar and wind turbine in particular. MATLAB/Simulink models of PV Solar and Wind Energy Conversion Systems are discussed in detail in the very last two chapters. There are very few books on this subject. This book tries to fill this gap and pursues the following aims:
• It provides the necessary descriptions and explanations of blocks, functions and models.
• It organizes the material in a logical sequence, from simple to complex, to make it easier to study MATLAB codes and Simulink library to enable this book to be used in the educational process covering various electrical fields.
The book can be used by students who are conducting research on Distributed Generations. It should also prove useful for graduate and undergraduate students undergoing courses in electrical fields in higher educational institutions.Graphical Abstract







